VMFL057
VMFL057
Radiation
and Conduction in Composite Solid Layers
Overview
| Reference |
C.M. Spuckler, R. Siegel. “Two-Flux and Diffusion Methods for Radiative Transfer in Composite Layers”. Journal of Heat Transfer, Vol 118, pp. 218-222, 1996 | |
| Solver | Ansys Fluent | |
| Physics/Models |
Radiation modeling with DO model, participating medium with gray-band absorption | |
| Input File |
| |
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
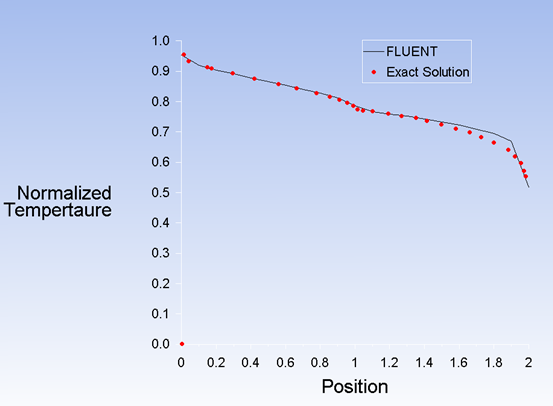
Test Case
Heat transfer by conduction and radiation is modeled in a composite solid domain consisting of two layers. Both the layers participate in radiation. The two layers are separated by a semi-transparent wall. The upstream and downstream sides of the domain are subjected to convective as well as radiative heat transfer.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Solid 1:
Solid 2:
|
Dimensions of the domain: 2 m X 1 m (the two solid zones are of equal length) |
Left-most wall:
Right-most wall:
|