VMFL011
VMFL011
Laminar
Flow in a Triangular Cavity
Overview
| Reference | R. Jyotsna, S.P. Vanka. “Multigrid Calculation of Steady, Viscous Flow in a Triangular Cavity”. J. Comp. Phys., Vol 122, pp. 107-117, 1995. | ||
| Solver | Ansys Fluent, Ansys CFX | ||
| Physics/Models | Viscous flow, driven by a moving wall | ||
| Input Files |
| ||
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
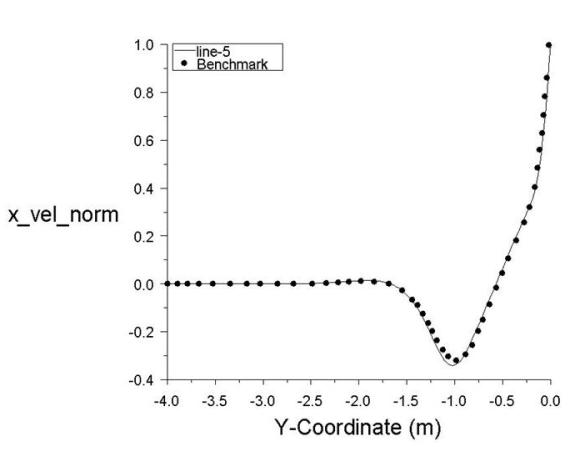
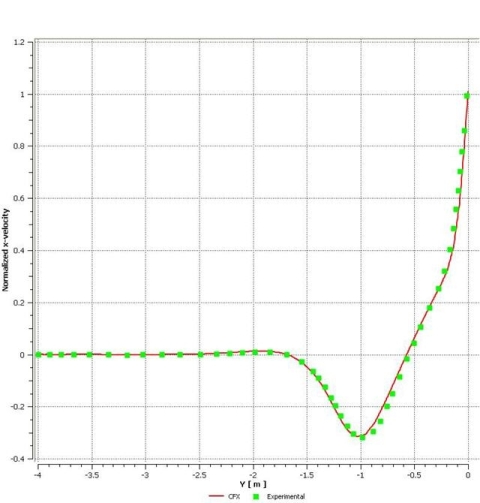
Test Case
Laminar flow induced by the motion of the top wall of a triangular cavity (Figure 20: Flow Domain). The side walls are stationary.
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density = 1 kg/m3 Viscosity = 0.01 kg/m-s |
Height of the triangular cavity = 4 m Width of the base = 2 m |
Velocity of the top (base) wall = 2 m/s Other walls are stationary |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The flow is steady. Pressure based solver is used. A hybrid mesh with triangular and quadrilateral cells is used to discretize the domain.