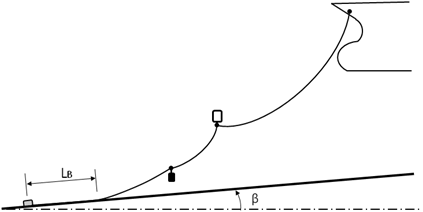
The quasi-static composite catenary model permits multi-segment elastic catenary lines, which can connect a body and the (sloped) sea bed, or join two bodies.
Each catenary segment is specified by its length, mass per unit length, equivalent cross-sectional area (which is numerically equal to the volume of water displaced per unit length of the line), and its linear or nonlinear axial stiffness properties. Intermediate buoys and clump weights can be attached at catenary segment joints. Two attachment points should be provided for each catenary segment. The sea bed slope may optionally be introduced if the mooring connects a body to the sloped sea bed. An example of a quasi-static composite mooring line anchored to a sloped sea bed is demonstrated in Figure 9.5: Composite Catenary Mooring Line.
In Figure 9.5: Composite Catenary Mooring Line, denotes the laid length of the mooring line on the seabed; the friction
force acting on this mooring line section is ignored.
An iterative procedure is involved in the simulation of a multiple-segment catenary mooring line fitted with intermediate buoys and clump weights, based on the catenary segment solution with either linear or nonlinear axial elasticity.
Current drag and inertia force on the quasi-static line itself are ignored.