VM295
VM295
One Dimensional Terzaghi's Consolidation Problem with Permeability as Function of
Depth
Test Case
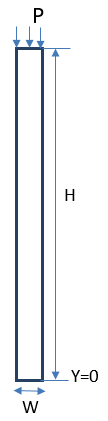
The test case is to simulate a one-dimensional Terzaghi's problem with permeability as a
function of the soil depth. A pressure P is applied on the top surface of the soil with depth
H and width W. The top surface of the soil is fully permeable and the permeability decreases
linearly with depth. The excess pore water pressure for 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 day is
calculated and compared against the reference results obtained using the PIM method (Figure 5,
pg. 5916).
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The soil is modeled using 2D CPT212 elements with plane strain
element behavior. The UX degree of freedom for all nodes is constrained and the UY degree of
freedom at the bottom of the soil is constrained. The pressure degree of freedom at the top
edge is constrained to make it fully permeable. Linearly varying permeability of the soil is
defined using the TB,PM material model. Static analysis is performed with
an end time of 86400 seconds (1 day) and with stepped pressure loading P on the top edge of
the soil. The excess water pore pressure at depth H = 6 m is computed for 0.1 (8640 s), 0.2
(17280 s), 0.3 (25920 s), 0.4 (34560 s), and 0.5 days (43200 s) by interpolating the solution
obtained at the nearest time points.