VM278
VM278
Effect of a Pipe Lying on the Ground Under Gravity Loading
Test Case
A straight pipe lies on the ground. Under gravity, the weight of the pipe creates pressure and a penetration of the ground surface. These quantities are determined from the contact output.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
|
Young’s Modulus, E = 2.0E11 Pa Poisson ratio, υ = 0.3 Density, ρ = 7850 kg/m3 Coefficient of friction, µ = 0.2 |
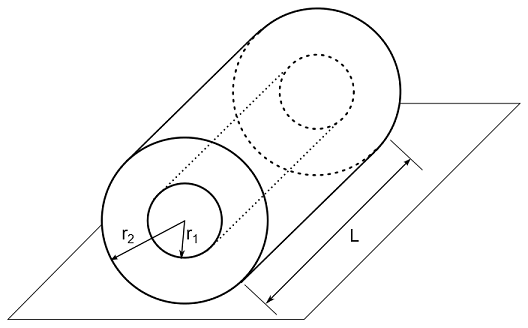
Length, L = 100 m Inner radius, r1 = 0.24 m Outer radius, r2 = 0.25 m |
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2 |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
PIPE289 elements are used to model
the pipe of length L = 100 m, outer radius r2 = 0.25 m, and inner radius r1 = 0.24 m.
The density of the pipe material is ρ = 7850 kg/m3. Based on this data, the weight of the cylinder
can be calculated as . The contact pressure is calculated by dividing the weight by the
area factor used in traction contact formulation. This area is the
product of the contact length and the outer radius of the pipe section:
. The
resulting contact pressure is
. The contact element is traction-based
(KEYOPT(3) = 1), so its stiffness (k = 1 x 106) is in units of force/length3. The formula
for penetration is:
.