VM212
VM212
DDAM Analysis of Foundation System (2-DOF System)
Test Case
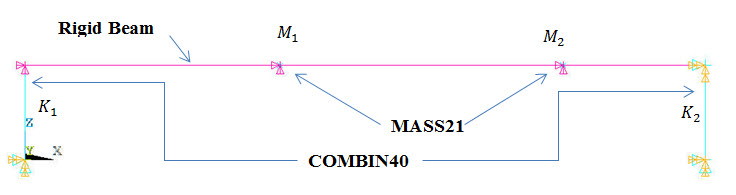
A simple equipment-foundation system is modeled using a spring-damper
element (COMBIN40) representing the foundation,
a beam element (BEAM188) representing the
equipment, and a mass element (MASS21) representing
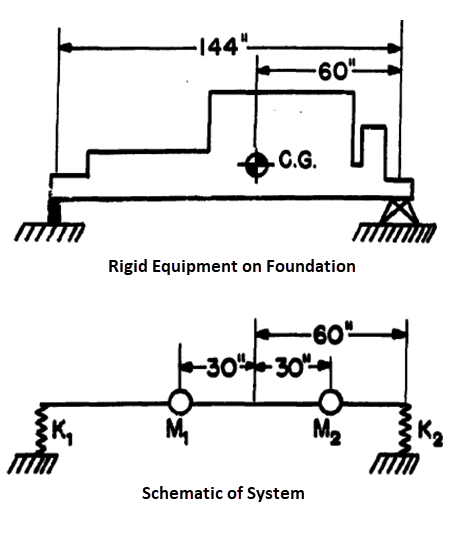
the equipment mass, as shown in Figure 336: Schematic Representation of 2-DOF System (Foundation System).
Shock loading is applied at the fixed base of the foundation
system along the athwartship direction. The shock spectrum is based
on the ship type, mounting location, direction of shock, and type
of design (elastic or elastic-plastic). DDAM analysis is performed
on this system to determine natural frequency, deflection, and shock
design value.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The equipment is assumed to be rigid. As only unidirectional
motion is being considered, the rigid equipment is divided into two
equal masses located about the center of gravity such that
 where Ig is the moment of inertia of the equipment at the center
of gravity and di is the distance to the mass
from the center of gravity.
where Ig is the moment of inertia of the equipment at the center
of gravity and di is the distance to the mass
from the center of gravity.
The fixed support condition is applied at the base of the foundation
system. At node 40, only UZ and ROTY DOF are being considered, while
other DOFs are constrained.
where Ig is the moment of inertia of the equipment at the center
of gravity and di is the distance to the mass
from the center of gravity.