MSHOPTIM
MSHOPTIM, --,
--, Level
Optimizes a selected mesh based on predefined finite element
specifications.
- --,--
Unused fields.
LevelLevel of mesh optimization.
-1
—
Conservative.
0
—
Standard (default).
1
—
Aggressive.
Notes
This action command tries to generate an optimum base mesh in the selected mesh region based
on the cross-sectional sizes of intersecting embedded elements. The cross-sectional area of line
embedded elements and the thickness of surface embedded elements define the cross-section sizes.
Use the Level field in the command to control the level of mesh
optimization.
The optimized base mesh can be used in subsequent reinforcing or direct element embedding modeling approaches to overcome simulation accuracy issues. In a reinforcing and direct embedding modeling approach, the base material and enclosed materials in a composite part can be independently discretized to produce separate base and embedded element meshes. Without proper meshing controls at the locations where the base and enclosed materials intersect (embedding regions), the simulation accuracy can be affected due to:
Base mesh overloading - The base mesh in embedding regions is overly refined. (For more details, see the EREINF command).
Base mesh underloading - The base mesh in embedding regions is insufficiently refined to accurately capture the high solution gradients often present at material discontinuities. (For more details, see the EEMBED command.)
Supported element types for the base mesh include:
| SOLID285: 3D 4-Node Tetrahedral Structural Solid |
| SOLID187: 3D 10-Node Tetrahedral Structural Solid |
| SOLID227: 3D 10-Node Coupled-Field Solid |
| SOLID291: 3D 10-Node Tetrahedral Thermal Solid |
Supported line and surface element types for the embedded mesh include:
| MESH200 as a lower-order line element (KEYOPT(1) = 2) with a discrete reinforcing section specified. |
| MESH200 as a lower-order triangle element (KEYOPT(1) = 4) with a smeared reinforcing section specified. |
| LINK33/LINK180/LINK228 with a “LINK” section specified. Higher-order elements LINK33/LINK228 (KEYOPT (4) = 1) are not supported. |
| BEAM188 with a “BEAM” section specified. |
Example Usage
To use the MSHOPTIM command:
Select the base mesh.
Select the line or surface elements that are partially or entirely enclosed in the base mesh. A cross section of these line or surface elements should be defined through section data.
Issue the MSHOPTIM command.
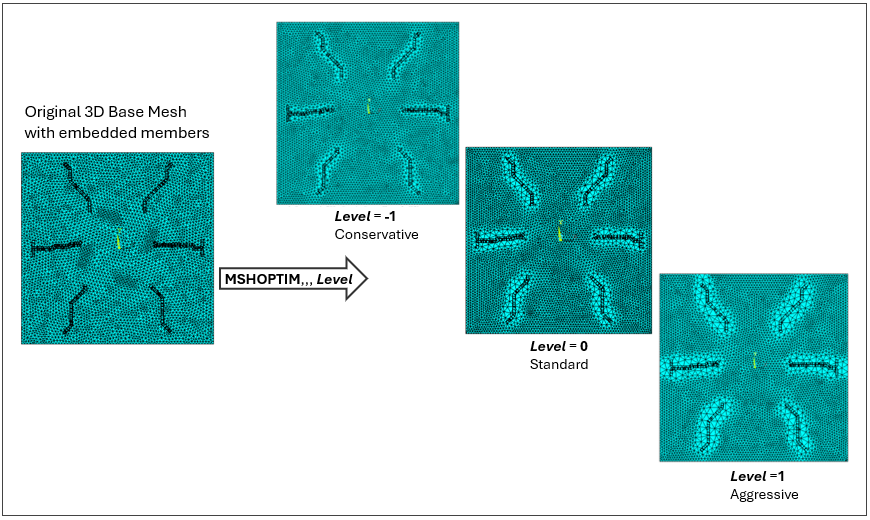
Example 1: Coarsening of the base mesh in a simple printed circuit board (PCB ) model
The following figure shows a very simplified printed circuit board (PCB) model where the
homogeneous dielectric board is modeled as 3D Tetrahedral solid elements (the base mesh) and the
enclosed metal traces are modeled as MESH200 elements with a discrete
EREINF section (the embedded mesh). The MSHOPTIM command is used with different values for Level
and the new meshes are shown for each Level option.
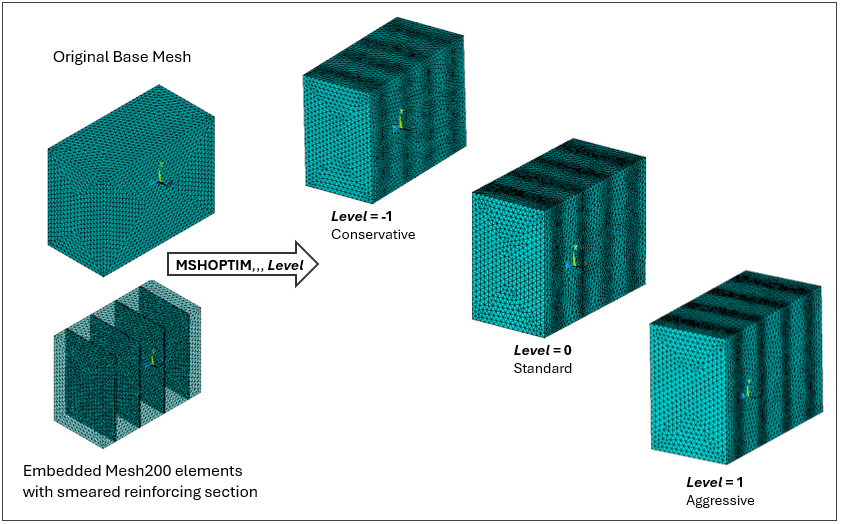
Example 2: Refinement of the base mesh based on selected MESH200 elements with smeared EREINF section
The following figure shows a simple block model that is modeled as 3D Tetrahedral solid
elements. It also has four surfaces meshed with MESH200 elements (KEYOPT
(1) = 4) with a smeared EREINF section. The MSHOPTIM
command is used with different values for Level and the new meshes are
shown for each Level option.
Limitations
When the MSHOPTIM command successfully optimizes the base mesh, it releases any associativity between the current solid model and the finite element model. This means that if the original finite element model was previously attached to any underlying geometry, it will no longer be so once the MSHOPTIM command successfully updates the base mesh. As a result, you will no longer be able to select, define, or clear finite element model items in terms of the detached solid model. This is the same as the MODMSH,DETACH command.
Loads, boundary conditions, connections, components, and so on, applied on the original base mesh are not transferred to the new base mesh.


