The solution object controls how results are imported into ACP-Post. Each solution links to a .rst results file. The import settings can be configured in the Solution Properties dialog. Solution Plots can be created in connection with a solution object. The solution set (for instance, load step) is specified for each plot object individually.
In Workbench mode, a solution is created in ACP-Post for every solution component that is linked to the ACP-Post cell in the project schematic. A solution can also be added by selecting Import Results in the context menu of the Solutions object in the Tree View. Doing so creates an individual solution and displays the Solution Properties dialog.
The context menu of every solution has the following options:
Properties: Display the Solution Properties dialog.
Update: Update the specific solution and reload result if changed.
Reload: Reload the results file.
Delete: Delete the selected solution.
Delete Postprocessing Results: Delete all deformations, stresses and strains, computed.
Export Results: Exports result (deformation, stress, strain, failure results, progressive damage) as a .csv file for selected Element Sets, oriented selection sets, and modeling plies for both shell and solid elements.
Create Deformation: Create a deformation plot for the selected solution. (see Solution Plots for more information on all plots)
Create Strain: Create a strain plot.
Create Stress: Create a stress plot.
Create Failure: Create a failure plot based on a failure definition.
Create Temperature: Create a temperature plot if data is available.
Create Progressive Damage: Create a progressive damage plot if data is available.
Paste: Paste a plot from the clipboard.
Import settings and load step selection can be configured in the Data tab of the Solution Properties dialog.
The following properties can be set in the Data tab of the Solution Properties dialog:
Note that in the previous figure, the solution sets are greyed out; the solution set selection happens at the plot level.
Name: The name of the solution, used in postprocessing.
Format: The format of the solution file to be imported.
Import an .rst result file from the Ansys solver. All solution information is contained in this file.
Import deformation and rotational result file. These files are generated by Mechanical APDL with the PRNSOL command.
File Path: When importing a .rst file, the path to that file. When importing individual deformation and rotational result files, the path to the deformation results.
Rotation Path: When importing individual deformation and rotational result files, the path to the rotational results (inactive otherwise).
Automatic Reload: When active, ACP checks for changes to result files and reads new results automatically.
Read Strains and Stresses: When importing a .rst file, import stresses and strains calculated by the solver by default. When this option is inactive and the Use ACP to Compute Strains and Stresses option is active, ACP calculates stresses and strains from deformation and rotation information present in the file. When several load steps or substeps are present, you are prompted to select which set is to be imported. Calculating stresses and strains with ACP can increase the computational load and time for postprocessing. So, it is only recommended for linear analyses. Interlaminar stresses and strains cannot be calculated for linear triangular elements in ACP.
Temperature Data Available: When active, this option indicates that the results file to be imported contains a temperature field. When imported, temperature data can be visualized, and temperature dependent material data can be used in stress and strain analysis.
Use Solid Results if Available: If this option is active and results for solid elements are present in the .rst file, the results are mapped onto the reference shell elements. Mapped results are visible when Solid Models are hidden. Postprocessing can be done on both layered shell and solid elements.
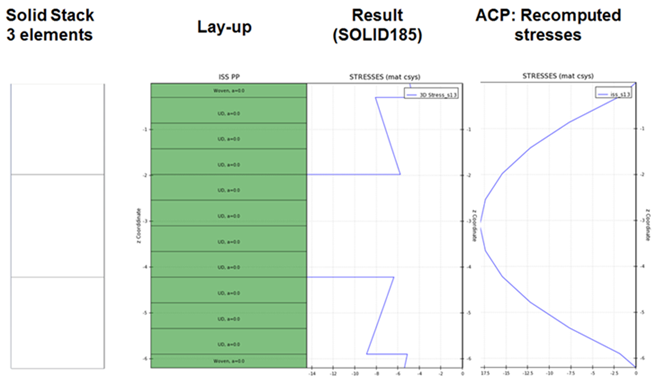
Recompute ISS of Solids: When active, ACP recalculates interlaminar shear stresses for solid models. The recomputation algorithm takes the following two steps:
Summation of all shear forces per solid stack.
Calculation of interlaminar shear stress by laminate-based approach (see Transverse Shear Stresses).
Non-zero boundary conditions are not considered in this recomputation process. The recomputed stresses take the place of the imported ones. The results file itself is not altered and the recomputation can be reversed by un-checking the option and updating the solution.