Unidirectional composites consist of fibers oriented in the same direction, surrounded by a matrix material.
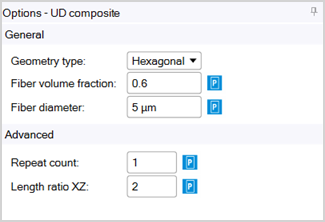
Geometry Type: Control the arrangement of fibers in cross section within the matrix.
Square: Cross section of fibers within RVE has fibers arranged as the vertices of a square.
Diamond: Cross section of fibers within RVE has fibers arranged as the vertices of a diamond.
Hexagonal: Cross section of fibers within RVE has fibers arranged as the vertices of a hexagon.
Note: In general, only the Hexagonal geometry type will lead to a transversely isotropic material.
Fiber Volume Fraction: The fraction of space within the RVE that the fiber material occupies.
Fiber Diameter: The diameter of the individual fibers in the active unit system.
Repeat Count: The number of times that the unit cell is repeated in each coordinate direction.
Length Ratio XZ: The ratio of the RVE length in the X direction divided by the length in Z direction.