Scattering Phase Function
Phase Function Definition
THe Scattering Phase Function corresponds to how particles scatter light according to the medium they are in.
Volumic diffusion is a physical process which occurs when a particle of material absorbs some energy of an incident electromagnetic wave, in the direction of propagation.
This energy is then redistributed around this particle according to a specific angular function which is called phase function.
This function has many parameters as the particle's size, wavelength, and the material and particle indexes.
According of Monte-Carlo propagation, this phase function can be assimilated to a probability for a photon which is propagated in 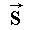 direction to be diffused in
direction to be diffused in 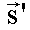 direction.
direction.
This function is named 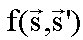 .
.
You can normalize this function with:
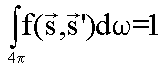
The following phase function corresponds to an isotropic diffusion:
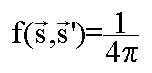
Anisotropy Factor
Anisotropy factor is available when Give scattering coefficient and phase function of the medium: Define phase function using Henyey-Greenstein formula, or Define phase function using a double Henyey-Greenstein formula is selected.
Anistropic factor g is when the phase function is not isotropic: -1 < g < 1.
- If g=0, rays can be propagated in all direction in the material.
- if g=1 there is a high probability that ray will propagate forward.
- if g=-1 there is a high probability that ray will propagate backward.
When the phase function is not isotropic, you must characterize isotropy with g parameter called Anisotropy factor with following definition:
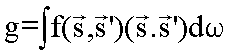
Alpha coefficient
Alpha coefficient is available with the Gegenbauer model when Give scattering coefficient and phase function of the medium: Define phase function using Gegenbauer formula is activated.
Alpha coefficient is an additional mathematical parameter of the anisotropic factor integrated in the Gegenbauer formula and used to find the best fit of the real scattering measurement that can vary according to wavelengths.
The Henyey-Greenstein model is a specific Gegenbauer model where a = 0,5.
Display
By selecting the View shading check box, you can display a shading view of the intensity envelope.
- By selecting the View Mesh check box, you can display the intensity envelope with wireframe.
By selecting the Decorations check box, you can display the 3D view tool.
For more details, you can view Using 3D view tool.
- By selecting the Axis System check box, you can display the axis system.
- You can edit 3D view preferences. For more details, you can view 3D View.
- By selecting the Logarithmic View check box, you can display the logarithmic view.


