Editing Distributed Machine Configurations
To edit an existing machine configuration:
-
Click Tools > Edit Active Analysis Configuration to open the Analysis Configuration dialog directly or click the Analysis Config icon on the Simulation ribbon.
This opens the Analysis Configuration dialog directly. You can also access this dialog from the HPC and Analysis Options window by clicking the Add..., Edit..., or Copy... buttons.
If you select Add... from the HPC and Analysis Options window, the fields are empty. If you select Edit... or use Tools > Edit Active Analysis Configuration, or click Copy from the HPC and Analysis Options window, the fields show the selected configuration:
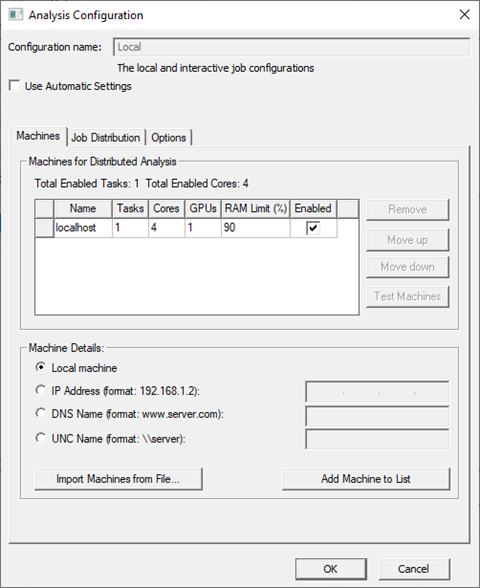
The option and features available differ for the various solvers.
Note: The GPUs column does not appear for Maxwell 2D solves. Use of GPUs is not currently supported for Maxwell 2D. -
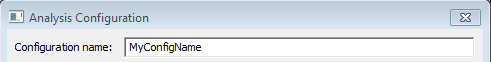
If you Add a new configuration, you must specify the name of the new or edited configuration. It cannot be empty and cannot be a previously used name or a reserved word.
-
If the solver supports automatic settings, you can select the Use Automatic Settings check-box to assign resources automatically, or you can uncheck the box to specify job distribution manually in the Job Distribution tab, as discussed below. For Maxwell, this setting currently is supported only for 2D and 3D Transient, and 2D and 3D Eddy Current designs.
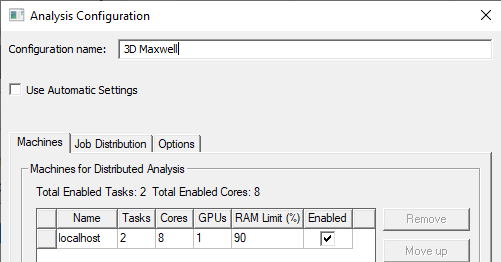
Selecting Use Automatic Settings removes the Job Distribution tab, which sets those parameters automatically based on the best use of available resources for the current analysis.
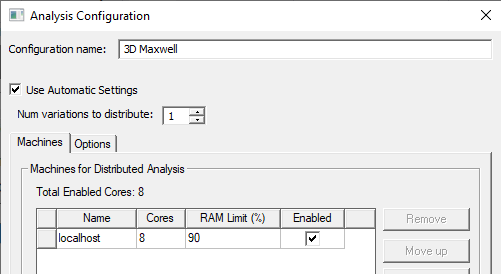
For Maxwell 2D and Maxwell 3D designs Use Automatic Settings must be checked to enable Num variations to distribute. In such cases, if you specify more than one, the distribution of variations is in proportion to RAM availability on the machines listed. Depending on the resources available, and whether the simulation defines Optimetrics variations and other distributed types, the simulation can include up to three levels of distribution. When you close the Analysis Configuration dialog box, the HPC and Analysis Options dialog Configuration Details field provides details of the Job Distribution for three-level distribution.
For 2D and 3D Transient designs, the Use Automatic Settings option distributes one excitation to each machine listed in the configuration. When this option is enabled, a minimum of two cores must be assigned. Each machine uses all cores assigned to it while solving its excitation. Unlike automatic frequency setup, the machines are assigned sequentially without regard to machine capability. For 2D and 3D Eddy Current designs with Use Automatic Settings, a minimum of four cores must be assigned.
Variations will not be distributed when the number of variations to distribute is set to 1. In this case when you close the Analysis Configuration dialog box, the HPC and Analysis Options dialog box, Configuration tab provides details of the Job Distribution that does not use three-level distribution.
-
The Machines Tab contains the machine list for the analysis configuration.
Here you can provide machine information, either by specifying Machine Details, or by importing a list of machines from a file. You can then remove, order, test, and enable machines on the list. Control buttons let you Add machine to List or Remove machines from the list.
Numbers of Tasks and Cores
If automatic settings are either not used or not available, note that each machine has an associated number of tasks and number of cores. The number of tasks specifies the total number of compute jobs that will be run on that machine simultaneously. Each separate solver, or distribution is one task. The total cores specifies the total number of cores that will be used on the given machine. This is how you specify multiprocessing. For example, if you want to run two threads for each task, you specify Total Cores = 2 x Number of Tasks. The number of cores must always be greater than or equal to the number of tasks. If the number of cores is not an exact multiple of the number of tasks, some tasks will use more cores than others. For example, if Number of Tasks is 4 and Total Cores is 10, 2 tasks will use 3 cores, and 2 tasks will use 2 cores.
GPUs
Note:- The GPUs column does not appear for Maxwell 2D solves. Use of GPUs is not currently supported for Maxwell 2D.
- The Electronics Desktop supports GPU acceleration only for Maxwell 3D Eddy Current Solution Matrix solves.
To enable use of GPU acceleration for Maxwell 3D solves, you set Enable GPU to True on the Options tab in the HPC and Analysis Options window (see Setting HPC and Analysis Options); and disable (uncheck) Use Automatic Settings in the Analysis Configuration window. The matrix solver automatically determines if all cores should be used, or if one GPU should be used to give the best performance. For example, for a Maxwell 3D Eddy Current Solution Matrix distribution, if you specify 4 cores for the simulation, the 3D eddy current solver will use 4 cores in parallel during matrix assembly while the matrix solver will use either 4 cores or 1 GPU.
RAM Limit (%)
Here you can specify the maximum percentage of the machine's RAM to be used for processing.
Import Machines from File...
You can import a machine list from a file, and an enhanced the file format handles the new flexibility. Each line of the file can contain a machine specifier of the form:
<MachineName>:<NumTasks>:<NumCores>
Note: this same format is used with the "-machinelist file=" command line option.
Local Machine Radio Button
To streamline the common case of running jobs on the current machine, use the dedicated radio button to specify the local machine.
-
To manually add each machine to the list, under Machine Details, specify an IP address, a DNS name, or a UNC name. Then click Add Machine to List.
The remote machines must have the same Ansys Electromagnetics Suite version installed in the same OS and version, and have the RSM service active.
Once you have specified the remote machine details, either directly or by Importing Machine from a File, you select a machine from the table to enable the buttons to Remove a machine, or to Move a machine up or down on the list.
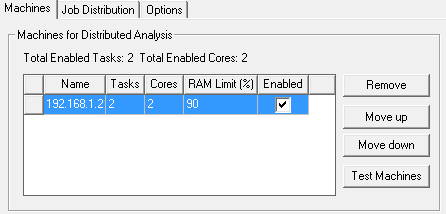
The displayed list shows the order in which you entered them irrespective of the load on the machines. If you have selected Use Automatic Settings, the Tasks column field is disabled because you no longer need to make those assignments. To control the list order, select one or more machines, and use the Move up or Move down buttons. Move up and Move down are enabled when you select one or more adjacent machine names.
Enabled Machines
Each machine on the current list has an Enabled checkbox. Here you can enable or disable the listed machines according to circumstance. Above the table, the dialog gives a count of the total enabled tasks, and the total enabled cores.
For distributed tasks, the software will allocate the total cores on a given machine to that machine's tasks. If a machine with 8 cores is running 2 distributed tasks, the software will automatically allocate 4 cores to each task. If it is running 4 distributed tasks, each gets 2 cores. And if it is running 3 distributed tasks, the first two tasks get 3 cores and the last task gets 2 cores.
For a given variation (for example, frequency or geometry), you should make assignments so that each task has the same number of cores. This is because the solvers attempt to make each task computationally balanced. For example, with two machines, one with eight cores, and another with four, assuming that the memory is proportionally equivalent, you could assign two tasks for machine 1, and one task for machine 2, giving all tasks the same number of cores.
In general, Ansys Electromagnetics Suite solvers use machines in the distributed analysis machines list in the order in which they appear. If you select a distributed configuration (rather than Local) on the ribbon Simulation tab, and you launch multiple analyses from the same UI, Ansys Electromagnetics Suite solvers select the machines that are running the fewest number of distributions in the order in which the machines appear in the list. For example, if the list contains 4 machines, and you launch a simulation that requires one machine, the solver chooses the first machine in the list. If another simulation is launched while the previous one is running, and this simulation requires two machines, the solver chooses machines 2 and 3 from the list. If the first simulation then terminates and another simulation is launched requiring three machines, the solver chooses 1, 4, and 2 (in that order)
Test Machines
Test Machines- When multiple users on a network are using distributed solve or remote solve, they should check the status of their machines before launching a simulation to ensure no other Ansys Electromagnetics processes are running on the machine. To do this, you can select one or more machines and click the Test Machines button. A Test Machines dialog opens.
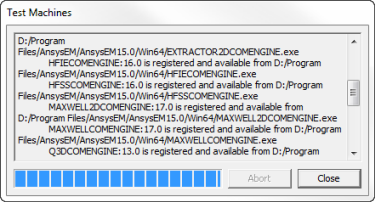
The test goes through the current machine list and gives a report on the status of each machine. A progress bar shows how far testing has gone. An Abort button lets you cancel a test. When the test is complete, you can Close the dialog box. If you need to disable or Enable machines from the list based on the report, you can do so in the Distributed Analysis Machines dialog.
Job Distribution Tab
Use this tab to manually enable specific job distribution types, and to enable multilevel solves. The Job distribution tab is disabled if you select Use Automatic Settings. Use this tab to manually enable specific types of job distribution and to enable multi-level solves.
Job distribution types are design type specific and will differ between solvers.
- Maxwell 2D and 3D design types can use Optimetrics Variations, Frequencies, Transient Solver, Solution Matrix, and Skew Model distribution types.
-
RMxprt can use only Optimetrics Variations.
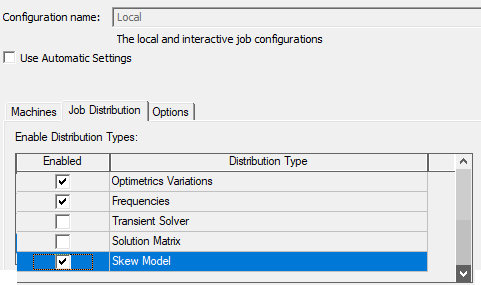
Use the check boxes to enable/disable available distribution types. The job distribution list box allows you to specify which job distribution types to allow for the current analysis configuration. At solve time, the Ansys Electromagnetics software automatically selects the best distribution type from the enabled distribution types. By enabling/disabling distribution types, you can control the job distribution.
Enabling a distribution type does not necessarily mean it will be used. It must also be allowed by the solve setup. For example:
- the Transient Solver distribution type that enables use of the Time Decomposition Method, will only be used with Maxwell 2D and Maxwell 3D transient designs.
- The Solution Matrix distribution type that enables use of the Matrix-based Domain Decomposition Method will be used with both 3D eddy current designs and 3D magnetostatic designs.
- The Skew Model distribution type for use with Maxwell 2D XY transient designs that use multi-slice skew models. Both single and two level distributions are supported.
Note that the enabled distribution types will apply to all setups of the given design type, so it is possible for different setups in a design to be solved using different distribution types.
The distribution types that you enable here are listed in the HPC and Analysis Settings dialog box in the Configuration details pane when select that configuration from the list.
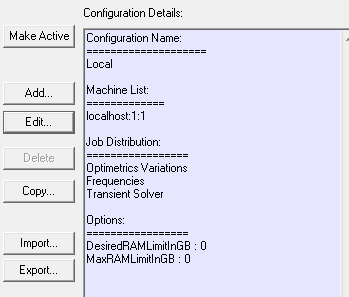
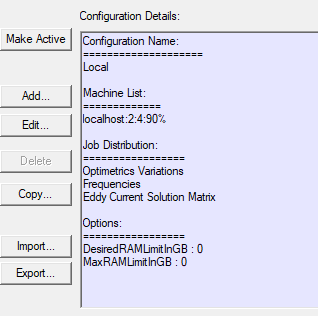
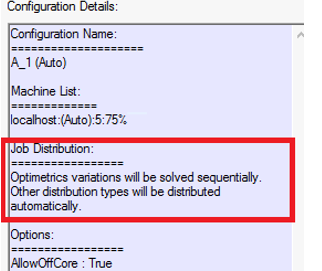
If your solver permits, and you have selected Use Automatic Settings, the Job Distribution notes that Optimetrics Variations will be solved sequentially. Other distribution types will be distributed automatically.
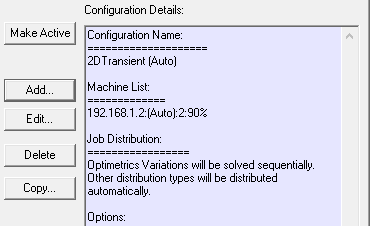
For products that support two-level distribution, when the design is appropriate, you can turn on two-level distributed solves, and specify the number of distributed solutions for level 1.
Distribution Levels
The radio buttons let you specify Single level only or Enable two level distribution.
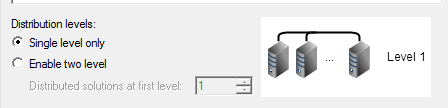
If you select Single level only, one distribution type will be applied at each stage of the solution process. If multiple types are available, the higher level solution will generally be distributed. All machine tasks will be used by the single-level distribution.
Single Level Distributions
Supported distribution types are Optimetrics Variations, Frequencies, Transient Solver, Solution Matrix, and Skew Model. Frequencies and solver distributions require MPI.
- Parallel distribution types such as Optimetrics Variations, and Frequencies are considered as not required. If these types are not able to distribute, the simulation can be run sequentially.
- Transient Solver, Solution Matrix, and Skew Model distribution types are considered as required. If these types are enabled the software will assume that distribution is necessary to extend the simulation scale or add fundamental solution capabilities.
-
When multiple distribution types are available, the higher level solution will generally be distributed. The priority order is : Optimetrics Variations, Transient Solver, Frequencies, Solution Matrix, and Skew Model. If Iterative Solver is enabled in the Eddy Current solve setup, the priority order will be: Solution Matrix, Optimetrics Variations, Transient Solver, and Frequencies. For example, Optimetrics Variations will be distributed when both Optimetrics Variations and Transient Solver are selected.
Two-Level Distributions
Selecting Enable two level enables the Distributed Solutions at first level selection box.
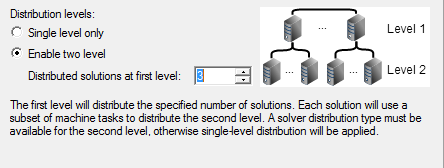
The first level will distribute the specified number of solutions. Each solution will use a subset of machine tasks to distribute the second level. The Transient Solver distribution type must be available for the second level for a Transient design; otherwise single-level distribution will be applied. The Solution Matrix or Frequencies distribution type must be available for the second level for an Eddy Current design; otherwise single-level distribution will be applied.
- Distribution types that can be distributed at Level 1 are Optimetrics Variations, and Frequencies(Maxwell 3D).
- Frequencies, Transient Solver, Solution Matrix (Maxwell 3D only), and Skew Model (Maxwell 2D XY transient only) distribution types can be distributed as Level 2.
The following are examples of a two-level distribution:
-
A parametric setup distributing Optimetrics Variations as level 1, and a Frequencies distribution as level 2.
- A parametric setup distributing Optimetrics Variations as level 1, and a Skew Model distribution as level 2.
Preview Job Distribution
The Preview Job Distribution Setup menu and field lets you view how the selected setup will be distributed.
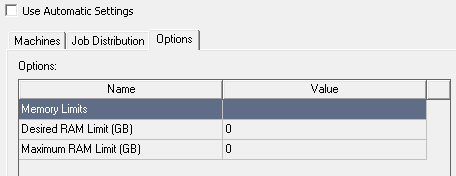
Options Tab (Analysis Configuration Dialog)
Use the Options tab to specify options for the current analysis configuration. Different design types may have different options available in their analysis configurations.
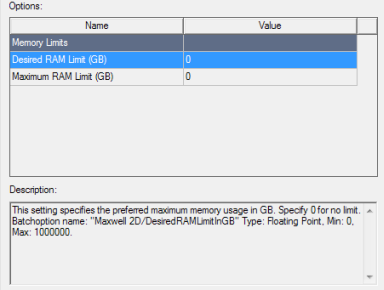
The Options grid contains the available option Names and editable Values.
These options settings will be in effect only when all the following are true:
- A design is being solved whose design type matches this analysis configuration's
- This analysis configuration is the active configuration for its design type
- You have not specified corresponding batch options on the command line. Command line batchoptions can be used to override the options specified by the active configuration.
Selecting an available option causes a display of a description of the option.
Relation to Batchoptions
Analysis configuration option settings can be overwritten by specifying the option name and value inside a -batchoption string. See -batchoptionhelp for a list of batchoption names and possible values. You can also view all available and frequently used batchoptions in the Job Management Submit Job To: dialog box, by clicking the Add... button under Analysis Options. This opens the Add Batchoption dialog box, which gives access to all batchoptions.
Adding Configurations or Accepting Edits
Click OK to accept the changes and close the Analysis Configuration dialog box. Only machines checked as Enabled appear on the distributed machines Configuration Details Machine list.
Regardless of the machine(s) on which the analysis is actually run, the number of processors and RAM Limit (%), the Desired and Maximum RAM Limits, and the default process priority settings are now read from the machine from which you launch the analysis. See Setting HPC and Analysis Options.
For more information, see distributed analysis.
Related Topics
Configuring Distributed Analysis
Editing Distributed Machine Configurations
Selecting an Optimal Configuration for Distributed Analysis
