Calculating the Properties for a Nonlinear Permanent Magnet
Nonlinear permanent magnet properties may be specified in one of two ways:
Input a B-H curve directly as follows:
- Click the View/Edit Materials… button in the Edit Libraries window.
- To define the nonlinear B-H curve, set
the Relative Permeability Type to Nonlinear:
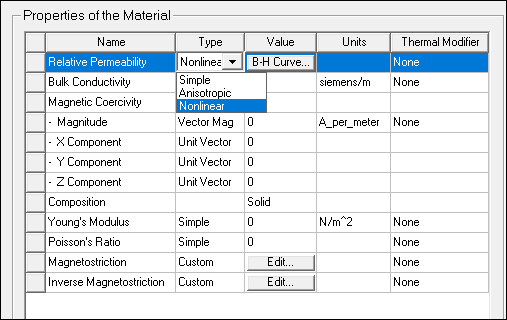
A B-H Curve button appears in the nonlinear property’s Value column.
- Input the B-H curve by clicking the B-H Curve button in the property Value column.
- For a Normal B-H curve, the slope of the curve can not be less than that of free space anywhere along the curve.
- For an Intrinsic B-H curve, the slope of the curve can not be less than 0.
- The Intrinsic B-H curve is supported only in Maxwell 2D/3D magnetostatic and transient design types. A material property defined using an Intrinsic BH curve will fail validation check in all the other product/design types.
- When an Intrinsic B-H curve is added, the Relative Permeability Value button label changes to Bi-H Curve as visual indication of the type of curve currently defined for the material.
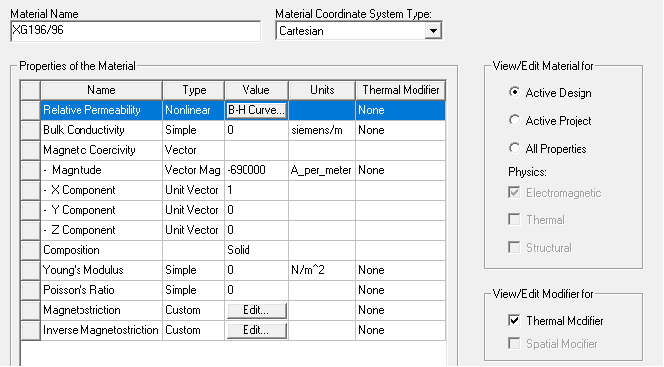
- To model a single temperature dependency for a nonlinear permanent magnet you must
- Use an Intrinsic B-H curve to model the Relative Permeability
- Specify
a thermal modifier for both Relative
Permeability and the Magnitude
of Magnetic Coercivity.
Apply a thermal modifier by selecting the Thermal
Modifier check box. Checking this box causes the Thermal Modifier column to display at
the right side of the Properties of the Material
table. Selecting Edit rather than
None causes display of the Edit Thermal Modifier dialog.
 Note: You can model multiple temperature dependencies of a nonlinear material property by providing two or more temperature-dependent BH curves. Refer to Specifying BH Curves for Nonlinear Relative Permeability for detailed information.
Note: You can model multiple temperature dependencies of a nonlinear material property by providing two or more temperature-dependent BH curves. Refer to Specifying BH Curves for Nonlinear Relative Permeability for detailed information.
The View/Edit Material window appears.
This opens the BH Curve dialog box in which you can input (or modify) curve data. (Refer to Adding Datasets for general information on working with datasets.)
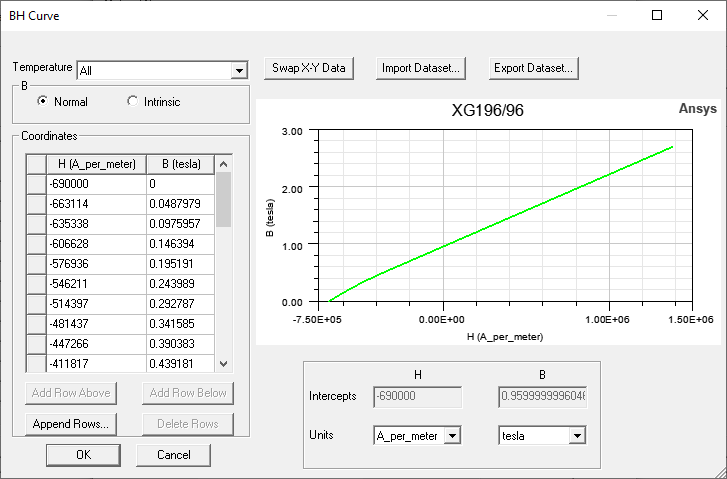
When you click OK in the dialog box, an error message displays if a slope is out of tolerance, identifying the data points between which the slope is less than that of free space.
The operations to input a nonlinear demagnetization curve are the same as entering a B-H curve for Steel material. When a B-H curve goes through the second quadrant or third quadrant, the curve is treated as a demagnetization curve.
Creating a Nonlinear B-H Curve with Four Parameters
Alternatively, a nonlinear B-H curve can be modeled by the following four parameters:
- residual flux density Br
- coercive field force Hc
- maximum energy product (BH)max
- relative recoil permeability mr
From the View/Edit Materials window:
- Set the Relative Permeability to Nonlinear.
- Select Nonlinear Permanent Magnet from the drop-down menu.
- Click OK to close the dialog box and return to the View/Edit Materials window.
This enables the Calculate Properties for... drop-down menu at the bottom of the window.
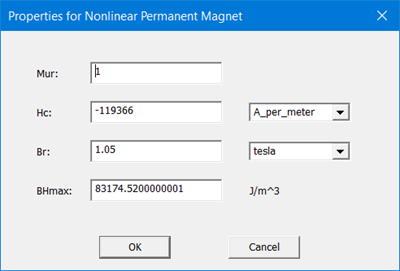
This displays the Properties for Nonlinear Permanent Magnet dialog box, which contains the following fields into which you enter the appropriate values.
|
Mur |
Provide a value for relative permeability. |
|
Hc |
Coercive field force Hc in the units specified. Provide a value and select units from the drop-down menu. |
|
Br |
Residual flux density Br in Tesla. If enabled, provide a value and select units from the drop-down menu. |
|
BHmax |
Maximum magnetic energy product (BH)max If enabled, provide a value and select units form the drop-down menu. |
The values for Relative Permeability and Magnitude under Magnetic Coercivity are updated as new default values, and the existing B-H curve is updated based on the new values of these parameters.
Related Topics
Nonlinear vs. Linear Permanent Magnets
Characteristics and Main Parameters of Permanent-Magnetic Materials
Calculating the Properties for a Permanent Magnet
Specifying B-H Curves for Nonlinear Relative Permeability
