Radiated Power Calculation Method
For design that contain only FEM objects, you can select the Radiated Power Calculation method. This can ensure that the radiated power result is continuous in a frequency range or parametric sweep. If the design contains surface regions (IE, PO or SBR+ regions) or linked fields (either a near field or far field link) the power calculation method commands do not appear.
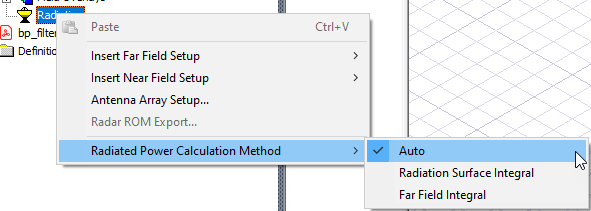
The default selection is Auto.
- For Auto mode, the rule is: When design has a single FEM region, we use radiation surface integral. When design has multiple disjointed FEBI regions, we use far field integral. Based on our studies, this rule can ensure the best accuracy for the majority of projects.
- For Radiation Surface Integral, near fields are integrated over each element on the radiation surfaces to obtain their contribution of radiated power, and then added together.
- For Far Field integral, far field is first calculated over a full sphere, and far fields are integrated over the sphere.
In some case, when the model is barely radiating, Far Field integral method may give better accuracy than Radiation Surface Integral method.
When Far Field integral is used, a correction factor is applied to Radiation Efficiency and Gain calculation (see Computing Antenna Parameters). The correction factor is equal to the ratio of the radiated power calculated from Radiation Surface Integral divided by the one calculated from Far Field Integral.
