Most digital devices, such as cellphones and tablets, include one or even several microphones. Micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) technology is very useful for designing these products due to their miniature dimensions (millimeters).
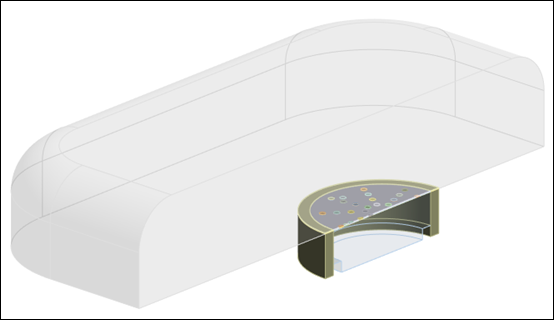
A MEMS microphone adheres to the condenser principle. It consists of two silicon-based electrodes separated by a thin air gap; one electrode is rigid (called the back plate), and the other is a membrane that deflects under sound pressure. The air gap acts as a dielectric material between the electrodes, and the capacitance varies as a function of the distance between the electrodes [1].
This example illustrates how to analyze the response of a condenser MEMS microphone.