VM-WB-MECH-072
VM-WB-MECH-072
Thermal Stresses in a Long Cylinder
Test Case
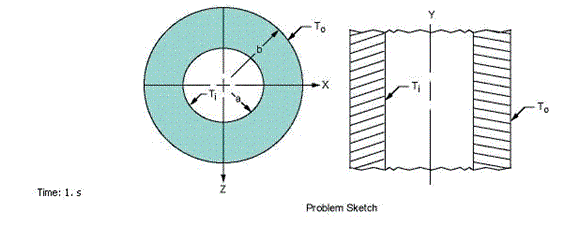
A long thick-walled cylinder is maintained at a temperature
Ti on the inner surface and To on the outer surface. Determine the temperature distribution through
the wall thickness. Also determine the axial stress σa and the tangential (hoop) stress σt at the inner and outer surfaces Edge sizing is used
for all edges and edge behavior is defined as hard.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes for Ansys Mechanical
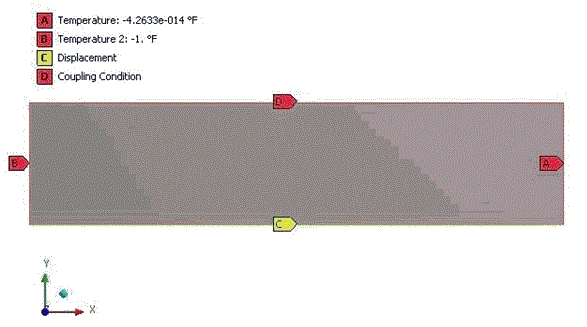
Because of the symmetry in loading conditions and in the geometry, this problem is solved as
an axisymmetric problem in Ansys Mechanical. The axial length is arbitrary and it is taken has 0.1 in.
Nodal coupling is used in the static stress analysis. Model is used for the thermal and stress
solutions.
Results Comparison for Ansys Mechanical