VM-WB-MECH-037
VM-WB-MECH-037
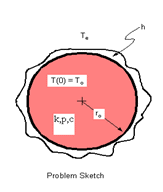
Cooling of a Spherical Body
Overview
| Reference: |
Kreith, F. (1959). Principles of Heat Transfer (2nd ed., pp. 143, ex. 4-5). Scranton, PA: International Textbook Co. |
| Solver(s): | Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Transient Thermal Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Plane |
Test Case
Determine the temperature at the center of a spherical body, initially at a temperature T0, when exposed to an environment having a temperature Te for a period of 6 hours (21600 s). The surface convection coefficient is h.
Initial temperature, T0 = 65 °F
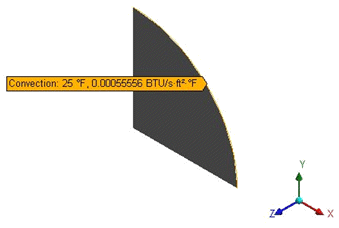
Surface temperature, Te = 25°F
Convection coefficient h = 5.5556e-4 BTU/s-ft2-°F
Time, t = 21600 seconds
Radius of the sphere ro = 2 in = 1/6 ft
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|