VM-WB-MECH-007
VM-WB-MECH-007
Thermal Stress in a Bar with Temperature Dependent Conductivity
Overview
| Reference: | Any basic Heat Transfer book |
| Solver(s): | Ansys Mechanical |
| Analysis Type(s): | Nonlinear Thermal Stress Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Solid |
Test Case
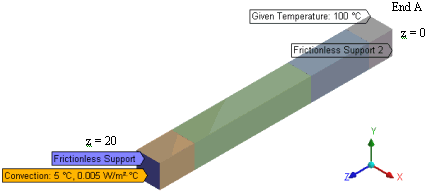
A long bar has thermal conductivity that varies with temperature. The bar is constrained at both ends by frictionless surfaces. A temperature of T °C is applied at one end of the bar (End A). The reference temperature is 5°C. At the other end, a constant convection of h W/m2 °C is applied. The ambient temperature is 5 °C. Advanced mesh control with element size of 2 m is applied.
Find the following:
Minimum temperature
Maximum thermal strain in z direction (on the two end faces)
Maximum deformation in z direction
Maximum heat flux in z direction at z = 20 m
Temperature at a distance z from rear face is given by:
Thermal strain in the z-direction in the bar is given by:
Deformation in the z-direction is given by:
Heat flux in the z-direction is given by:
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | Conductivity (W/m °C) | |||||||||||||
| 5 | 3.91 x 10-2 | |||||||||||||
| 800 | 0.215 | |||||||||||||
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes for Ansys Mechanical
The following figure shows the finite element model in Ansys Mechanical:
Results Comparison for Ansys Mechanical
| Results | Target | Mechanical | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum Temperature (°C) | 38.02 | 38.014 | -0.017 |
| Maximum Thermal strain (z = 20) (m/m) | 0.000495 | 0.0004952 | 0.041 |
| Maximum Thermal strain (z = 0) (m/m) | 0.001425 | 0.001425 | 0.000 |
| Maximum Z Deformation (m) | 0.00232 | 0.002341 | 0.914 |
| Maximum Z Heat Flux (z = 20) (W/m2) | 0.165 | 0.16507 | 0.042 |