VM-EXD-MECH-001
VM-EXD-MECH-001
Flow of Gas Past an Infinite 2-D Wedge
Overview
| Reference: | Harlow, Francis H. et al., Fluid Dynamics – A LASL Monograph, LA-4700, June 1971. |
| Analysis Type(s): | Explicit Dynamics 2-D |
| Elements: | Multi-material Euler Quad |
| Boundary Conditions: | Euler Outflow, Default Wall |
| Structural Interactions: | No |
| Fluid-Structure Interactions: | Yes, fully coupled |
| Bonds: | No |
| Materials: | Ideal Gas |
Test Case
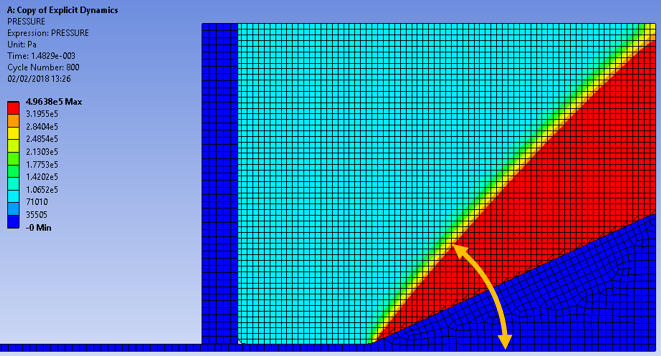
Perform a dynamic flow analysis of a Mach 2 gas flowing past a 2-D wedge until a steady-state configuration is obtained. An attached shock is formed, the angle of which is determined by the flow conditions.
Because the appearance of the configuration is independent of magnification, there is no significant length to the system.
Calculation Description
The scenario is modeled as a rigid piston pushing a column of ideal gas over the wedge. The top boundary is set to rigid to prevent the gas from flowing out from there. At the bottom, the gas is contained by the geometry. At the right is a Euler outflow boundary.
The initial conditions for the Ideal Gas in both parts are:
| γ = 1.4 |
| ρ = 0.001 gm/cc |
| p+ = 100 MPa |
| I0 = 2.5E5 J/Kg |
| ux = 1000 m/s |
The calculation is run for 3000 cycles, by which time a steady-state condition is achieved.