Thermal strain is computed when coefficient of thermal expansion is specified and a temperature load is applied in a structural analysis. To specify the coefficient of thermal expansion, you must set Thermal Strain Effects to Yes in the Details of the part or body objects before initiating a solve.
Each component of thermal strain is computed as:
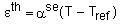
Where:
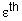 - thermal strain in one of the directions x,
y, or z.
- thermal strain in one of the directions x,
y, or z.
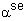 - Secant coefficient of thermal expansion
defined as a material property in Engineering Data (see "Chapter 2.4 Linear Material
Properties" in the Element Reference of the Mechanical APDL application Help for more information about
the secant function).
- Secant coefficient of thermal expansion
defined as a material property in Engineering Data (see "Chapter 2.4 Linear Material
Properties" in the Element Reference of the Mechanical APDL application Help for more information about
the secant function).
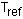 - reference temperature or the
"stress-free" temperature. This can be specified globally for the model using
the Reference Temperature field of Static Structural or Transient Structural analysis types.
Optionally you can also specify the reference temperature as a material property for cases
such as the analysis for cooling of a weld or solder joint where each material has a
different stress-free temperature.
- reference temperature or the
"stress-free" temperature. This can be specified globally for the model using
the Reference Temperature field of Static Structural or Transient Structural analysis types.
Optionally you can also specify the reference temperature as a material property for cases
such as the analysis for cooling of a weld or solder joint where each material has a
different stress-free temperature.


