Deviation control enables you to set the mesh resolution in the primary curvature direction for fillets on shell (surface) bodies. Mesh resolution along the fillet is taken from global or local mesh size controls. Deviation control enables you to scope faces or face based named selections.
All Deviation bodies should be scoped under Automatic (PrimeMesh) method. If not, scope the bodies under Automatic (PrimeMesh) to perform Deviation operation.
To access the Deviation control,
Right-click Mesh object and click Insert > Deviation.
or
Click Mesh on the Tree Outline and click Deviation in the Mesh Context tab on the Ribbon.
When you click Deviation, the Details view displays the deviation options:
Scope
Scoping Method: Allows you to select the scoping method for Deviation control. The default method is Geometry.
Geometry: Allows you to scope the faces.
Named Selection: Allows you to scope the face based named selection.
Definition
Suppressed: Allows you to suppress the Deviation control. The default value is No. When Suppressed is set to Yes, the Active field displays the status of the Deviation control. The Active field is read-only.
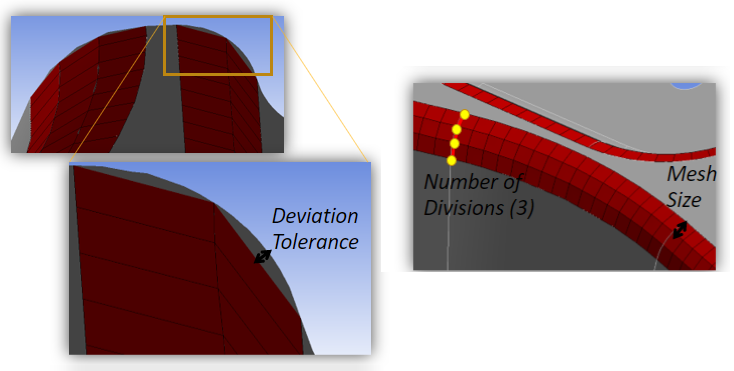
Type: Allows you to define the type of deviation control specifications. The available options are Deviation Tolerance, Mesh Size, Number of Divisions.
Deviation Tolerance: Allows you to specify the maximum distance between the mesh and the curvature of the fillet. You can provide smaller Deviation Tolerance to get a better curvature resolution.
Mesh Size: Allows you to specify the mesh size on the shorter sides of the fillets. The default value for Mesh Size is 75% of the chosen Element Size.
Number of Divisions: Allows you to specify the number of divisions on the curved sides of the faces.
Limitations
In the Mesh Details view, when the Capture Curvature is set to Yes, the Deviation control is not considered while meshing.
Deviation control supports only quadrilateral mesh.
Deviation control does not work on fillets having sharp angle edges.
Deviation control only meshes continuous body. It does not mesh any exclusion or inclusion in the model.
When Deviation control cannot be applied, the default quadrilateral dominant mesh is generated.
When there is an extra topological node on one side of the shorter edge of the fillet, the node gets projected to the other shorter edge of the fillet to get all quadrilateral mesh for Deviation control.
The Deviation control generates quadrilateral mesh on triangular and polygonal shaped fillets.


