Automatic (PrimeMesh) performs sweeping for solid models and generate quadrilateral elements for sheet body models, when Solid-Shell Weld - Shared Nodes is No under Meshing option in Files > Options > Meshing. When solid bodies cannot be swept, the body is meshed with the Patch Conforming Tetrahedron mesher. Automatic (PrimeMesh) creates non conformal mesh with contacts between the shell and the weld bodies.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) performs tetrahedral mesh for solid bodies even though bodies are sweepable and quadrilateral mesh for the sheet bodies, when Solid-Shell Weld - Shared Nodes is Yes under Meshing option in Files > Options > Meshing. Automatic (PrimeMesh) creates conformal mesh with contacts between the shell and the weld bodies.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) method can be scoped to all body types like solid, sheet and beam bodies. Automatic (PrimeMesh) uses global Element Order for meshing.
When Solid-Shell Weld - Shared Nodes is set to No,
Geometry operations such as Repair Topology, Connect and so on are not performed on the solid bodies which are scoped to the Automatic (PrimeMesh). For example, when you perform Repair Topology with merge face operation on two faces of the solid bodies, that operation is not executed.
Weld generation between shell and solid bodies can be completed but the node connection between the weld and solid bodies are not conformal. Instead, contact is created during the solve.
When Solid-Shell Weld - Shared Nodes is set to Yes,
Geometry operations such as Repair Topology, Connect and so on are performed on the scoped solid bodies which are scoped to the Automatic (PrimeMesh).
To access Automatic (PrimeMesh),
On the Tree Outline, right-click Mesh and click Insert > Method.
Or
On the Tree Outline, click Mesh and click Method in the Mesh Context tab on the Ribbon.
For sheet bodies, Select Method as Automatic (PrimeMesh) in the Quadrilateral Dominant Details view.
Scope
Scoping Method: Allows you to scope geometry bodies or named selection. The default value is Geometry Selection.
Geometry Selection: Allow you to scope the geometry bodies. When you select Geometry Selection, the Geometry allows you to select the geometry from the Geometry window.
Named Selection: Allow you to scope bodies grouped under a named selection.
Definition
Suppressed: Allows you to suppress the selected control. The default value is No. When Suppressed is set to Yes, Active displays the status of the selected control. Active is read-only.
Method: Allows you to select method.
Control Messages: Provides an error message for errors or incompatibilities in the scoped geometries of the method. Control Messages is available only when Use Adaptive Sizing is set to Yes, the input geometry has symmetries or two Automatic (PrimeMesh) method is scoped to the same body. You can click Control Messages to view the error message.
Advanced
Shell Mesh Type: Allows you to select the type of shell mesh. The default value is Quadrilateral.
Triangle: Allows you to generate a triangular mesh for shell bodies.
Quadrilateral: Allows you to generate a quad-dominant mesh for shell bodies.
Triangle Reduction: Allows you to reduce the number of triangular elements while meshing with Quadrilateral mesh type. The available options are None, Conservative, and Aggressive. The default option is Conservative. Triangle Reduction is available only when Shell Mesh Type is Quadrilateral.
None: Allows you to generate quadrilateral mesh without reducing the triangle count on the whole body.
Conservative: Allows you to move the triangles near to the boundary nodes or edges away from the boundary and then reduces the triangle count on the whole body.
Aggressive: Allows you to move the interior triangles and the boundary triangles to form pairs of connecting triangles and then reduces the triangle count on the whole body. Hence, Aggressive removes more triangles than Conservative.
Note: Aggressive may reduce the quality of the mesh while removing triangles.
Auto Repair Topology: Allows you to automatically repair topologies of the scoped bodies, when set to Yes. The default value is No. The available options are:
Remove Thin Faces: Removes the thin faces by merging them with the neighboring faces below the specified tolerance. When Remove Thin Faces is Yes, the available option is :
Thin Face Width: Allows you to specify the width of the thin face. The default value for Thin Face Width is same as the Connection Tolerance.
Collapse Short Edge: Collapses the edges below the specified tolerance. Feature edges and Protected edges are not collapsed. The default value is No. When the Collapse Short Edges is Yes, the available option is:
Short Edge Length: Allows you to specify the shortest edge length to perform collapse operation. The default value for Collapse Short Edges is same as the Connection Tolerance.
Remove Sharp Angle Faces: Removes the sharp angle faces below the specified angle tolerance by merging them to the neighboring faces. The default value is No. When Remove Sharp Angle Faces is Yes, the available option is:
Sharp Angle: Allows you to capture faces below the specified angle. The default value for Sharp Angle is 10 degrees.
Feature Angle: Specifies the minimum dihedral angle at which the geometry features are repaired. The default value is 30 degrees. You can provide any value between 0 to 180 degrees.
Feature Angle is the dihedral angle measured as follows:
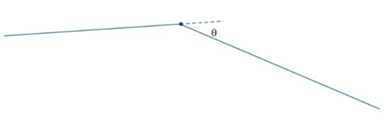
When θ = 0, two surfaces are perfectly tangential, and the edges are not protected. Hence, the two surfaces can be merged, or edges can be suppressed, pinched or more.
When 30 ≤ θ ≤ 90 degrees, the edges between the two surfaces are protected and cannot perform merging or pinching at the location.
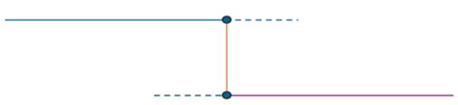
θ = 90
When θ > 90 degrees,the surfaces are not protected and prevents topology operations like merge or pinch on faces or edges.
Note: When you scope same body or part with the Auto Repair Topology and Repair Topology, the Message window displays a warning message that multiple repair topology options overlap. Software executes controls with the smallest values first, which can lead to unexpected result.
Best Practices
The recommended inputs for Automatic (PrimeMesh) are as follows:
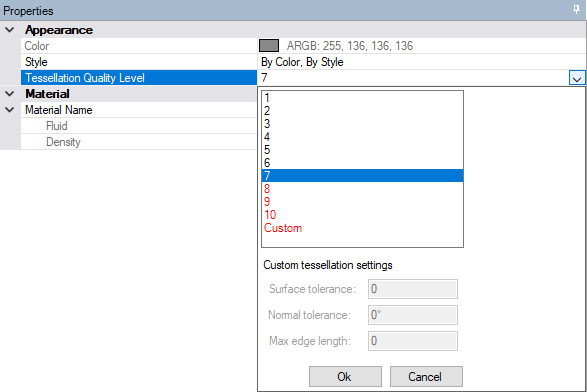
Set the facet quality to 7 before importing model into Mechanical. You can set the facet quality in SpaceClaim by navigating through . The facet quality in DesignModeler can be set by navigating through .
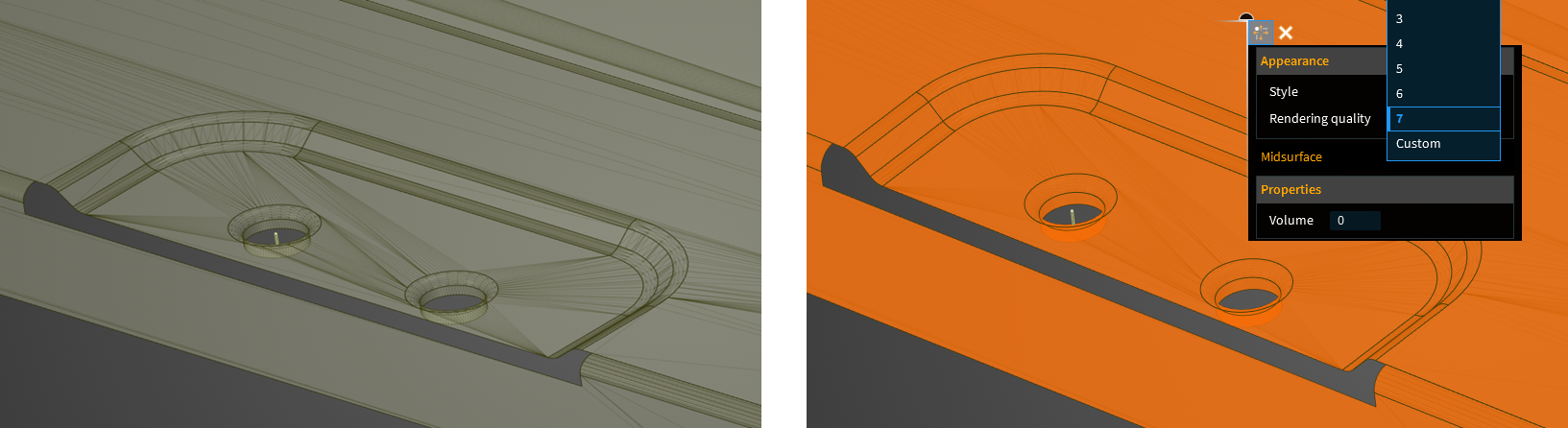
For bodies with large cylindrical faces, a facet quality of 10 may be required for adequate geometric representation during meshing. To avoid rendering the whole model with this value, you can set this value on each body using Body Properties in SpaceClaim or under Appearance in Discovery.
In SpaceClaim, DesignModeler, or in other upstream CAD package, Extend operation should be performed. The largest connection gap to be resolved should be smaller than the specified Element size.
Remove overhangs in upstream CAD. Overhangs are small penetrations between two surfaces. When unresolved overhangs can lead to mesh failure or mesh quality issues.
Imprinting edges or performing share topology at CAD level is not recommended. If CAD model has edges already imprinted, then use Repair Topology to remove them.
If the model has faces with missing facets, then you should fix them in upstream CAD.
The suggested general connection strategy is for clean models that do not have much difference between the smallest and the largest gap to be connected across. The best practices to follow while connecting two entities are as follows:
Find the smallest and largest gap between the entities to be connected.
Define a list of connection tolerance such that the smallest gap is less than the smallest connection tolerance and the largest connection tolerance is greater than the largest gap.
Check for any warning message on unconnected edges reported during meshing.
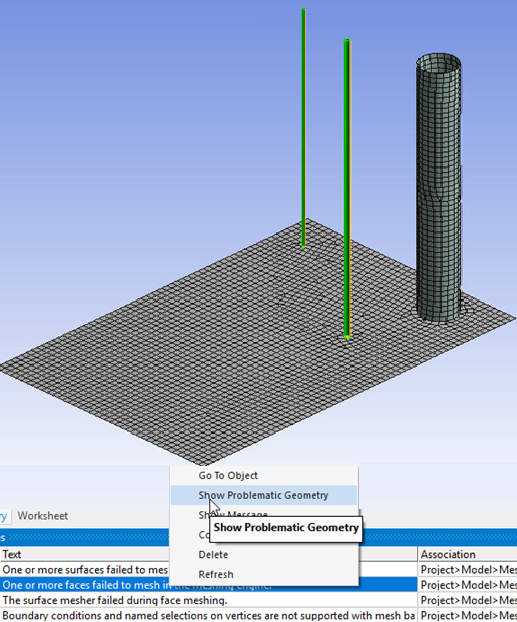
Right-click the warning message and select Show Problematic Geometry. Use model Walk to analyze the unconnected regions.
Create named selections on unconnected entities.
Remember the following while performing Automatic (PrimeMesh):
The gap size between the entities to be connected must be smaller than the Element Size. For example, if the biggest gap size to be resolved is 1 mm then the element size must be greater than 1 mm.
Faces (width) and edges (length) of the connected entities below the connection tolerance(s) are defeatured.
Mesh is not associated with defeatured entities (edge, face, body/part).
Mesh is not associated with vertices.
In Automatic (PrimeMesh), the Sheet Loop Removal only works if the connection is made through the Connect control.
In case of quadrilateral mesh failure, triangle mesh is generated with a warning message displayed.
Right-click the warning message and select Show Problematic Topology to display the bodies on which triangle mesh was generated.
If triangle mesh also fails, then the mesh failure is reported and CAD facets will be displayed.
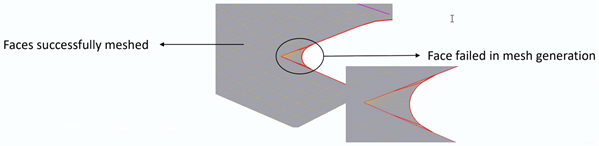
Limitations
The limitations of Automatic (PrimeMesh) are as follows:
Overlapping beams are not supported. Mesh in the overlapping portion of the beams will be assigned to either one of the involved beams.
Mapped Meshing does not support mapping of annular region.
Weld and Mapped control override all other sizing and local control settings.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not support multi-body parts which includes solid body parts.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not create conformal meshes between solids.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not support Layered Tetrahedrons Method.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not support global Defeature Size, when Mesh Defeaturing is set to Yes in the Sizing option. In Automatic (PrimeMesh), you must use Repair Topology to defeature the geometry. Also, in Repair Topology set Repair Thin Faces Options and Repair Short Edges Options to Yes for automatically repairing short edges and thin faces.
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not support Inflation control, Match control, Pinch control, Adaptive Sizing, BOI Size, Vertex Size (Sphere of Influence).
Automatic (PrimeMesh) does not support quality targets provided to the mesher.
Ease of Use Features
When an error or warning such as unconnected edges or mesh failure occurs, you can right-click the corresponding message and select Show Problematic Geometry to highlight the location at which error occurred in the model.
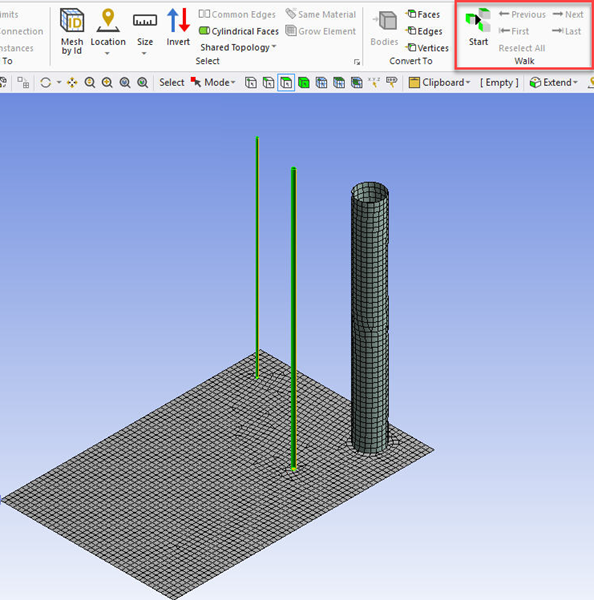
You can click Selections tab in the ribbon and click Start in Walk group to walk through the error locations. You can use Next to walk to the next location. You can click Previous to go back to the previous error location.
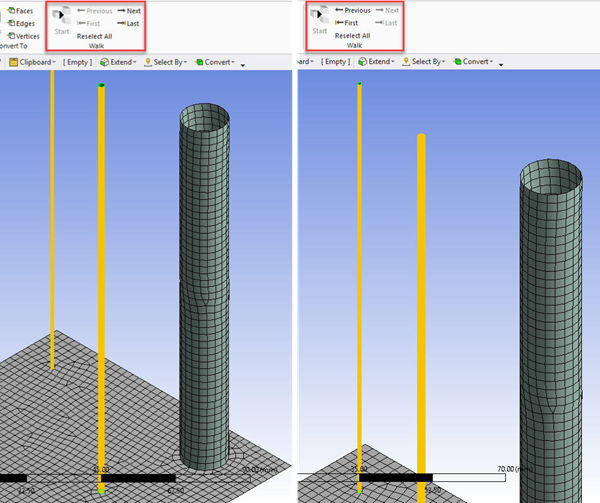
You can view the unconnected faces after meshing. To view the unconnected faces, right-click the Geometry window. Select Diagnostics > Find Unconnected Faces. The unconnected faces get highlighted in the model.
When entities scoped to Named Selection with Protected set to Yes are modified while performing Automatic (PrimeMesh), you will receive a warning message.


