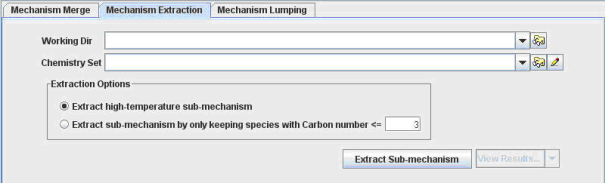
Mechanism Extraction is the second tab within the Mechanism Utilities panel of the Reaction Workbench interface, as shown in Figure 2-5. Reaction Workbench provides two types of mechanism-extraction utilities that are designed for reducing the size of very detailed and comprehensive hydrocarbon fuel-combustion mechanisms, based on some simplifying assumptions about the application of the mechanism. The two options are:
High-temperature extraction or removal of low-temperature kinetics pathways.
Carbon number extraction.
The high-temperature extraction retains all of the mechanism detail necessary for a high-temperature application (above ~1100 K) from a more complete full mechanism. It removes species and associated reactions that are known to be relevant only in low-temperature conditions. The carbon-number extraction removes any species that have a carbon number greater than the specified value, along with their associated reactions.
For the high-temperature extraction, the rules for identifying species that are relevant only in low-temperature conditions (and therefore removable) are as follows:
The number of Carbon atoms in the species is greater than 2. In this way the utility will make no modification to the C0-C2 core sub-mechanism of a full mechanism.
The species contains one of:
-OO radical group or
-OO group or
2 =O groups or
A ring structure with O.
These rules are applicable for extracting high-temperature sub-mechanisms from hydrocarbon fuels and for oxygenated hydrocarbon fuels.
To perform a high-temperature extraction, simply select the full mechanism chemistry set on which you wish to operate, choose the Extract high-temperature sub-mechanism option, and then click the Extract Sub-mechanism button. After the extraction is complete, you can use the pull-down menu to the right of this button to view the resulting (extracted) mechanism as well as a log file that reports what species and reactions were removed.
For the carbon-number extraction, the utility simply removes any species that contains more carbon atoms than the number specified. The maximum carbonnumber desired is specified in the text box to the right of the Extract sub-mechanism by only keeping species with carbon number <= label, when this option is selected. The number of carbon atoms in each species is determined by the thermodynamic data in the chemistry set, which provides the chemical composition of each molecule.
To perform a carbon-number extraction, select the full mechanism chemistry set on which you wish to operate, choose the Extract sub-mechanism by only keeping species with carbon number <= option, enter the number of carbon atoms to keep, and then click the Extract Sub-mechanism button. After the extraction is complete, you can use the pull-down menu to the right of this button to view the resulting (extracted) mechanism as well as a log file that reports what species and reactions were removed.