
This node is used for input
parametrization of batch script (*.bat and
*.cmd) files. The environment variable
%ComSpec% is considered when preparing the script execution and
can be used to choose a certain command line interpreter.
Script Tab
Use the file selector to open a batch file. The contents of the file are displayed in the text field. Any parameters that are auto-detected in the script are displayed in the table below the text field. You can drag these parameters from the table and drop them in the Parameter or Input Slots panes.
To tag text from the script file as a parameter:
In the text field, highlight the text to tag.
Right-click the text and select from the context menu.
In the dialog, optionally change the default parameter name and select whether to register the text as a parameter or an input slot.
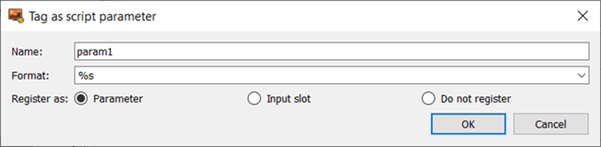
Click .
Input Files Tab
Displays a list of input files. The working file name can be relative or absolute.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
 | Adds an input file to the list. |
 | Removes the selected input file. |
| Input file path/slot name | Sets the location of the input file.
A copy of the file is stored in the working directory. |
Output Files Tab
Displays a list of all output files.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
 | Adds an output file to the list. |
 | Removes the selected output file. |
| Working file name |
Defines the working file name. The working file name can be relative or absolute. If the file exists only once in the design directory, only the file name is defined. If the file exists in several subdirectories of the design directory, you should define the relative path. You can use RegExes as working file names. To do so, select from the menu to the left of the field. When selected, the archival option is selected for all files that comply with the regular expression. Wildcards are not regular expressions. The following is a list of the most important conversions for wildcards and some examples for RegExes.
|
| Importance |
Defines the importance of files using the following options.
You must specify the maximum runtime in the additional options when using the and settings. These settings wait at most until the expiration of this value, even if the (executed) process has already finished. By default, conditions are checked every one second. The interval of the check can be changed in the configuration settings. If only one of or is set, but the associated files are not created, the process node waits until the maximum runtime. |
| Archival | Sets the type of file archiving.
|
| Slot name | By default, the slot name is the file name but it can be changed manually. |
Environment Tab
Displays a list of all environmental variables with their values.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
 | Adds an environment variable to the list. |
 | Removes the selected environment variable. The override for a default environment variable is removed or the variable entry is removed entirely if it does not exist in the default environment. |
| Default environment | Sets the conditions for the default environment variables.
|
| Prepend project directory and its bin subdirectory to PATH | When selected, two directories are inserted in front of the
PATH variable. For example, if your project path is
C:\mypath, the variable PATH will be
PATH = C:\mypath; C:\mypath\bin; C:\Windows
instead of PATH = C:\Windows |
Execution Settings Tab
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Designs per process |
When selected, activates the launch of a single process for multiple designs. The process node creates a file with designs to be calculated and provides the following environment variables for the executing script:
If this option is enabled, the environment variables
An example implementation for the script in process node: REM This is a Windows batch script (*.bat) copy ..\..\..\py\run_multi_cpfunc.py python run_multi_cpfunc.py %OSL_DESIGNS_BASE% %OSL_DESIGNS_LIST% An example code snippet to process the designs: # This is the Python script "run_multi_cpfunc.py"
...
basedir=normpath(sys.argv[1]) # base directory
listfile=normpath(sys.argv[2]) # path of the file containing the listing of design folders
for folder in listfilereader(listfile):
pd=myreader(join(basedir,folder,'inp_cpfunc.txt')) # pd stands for parameter dictionary
results={'Y': 0.5*pd['X1']+pd['X2']+0.5*pd['X1']*pd['X2']+5*sin(pd['X3'])+0.2*pd['X4']+0.1*pd['X5']}
mywriter(join(basedir,folder,'out_cpfunc.txt'),results)
...
|
| Ignore process exit code | When selected, ignores the process exit code, avoiding problems if the code is not evaluable. |
| Distinct working directory | When selected, creates an extra directory in the design directories for calculations. |
| Execute through command shell | When selected, interprets the command line or the script as a
shell command. When cleared, the process is started at the
operating system level. Note:
|
Run Options
This node has general Run Options. The number of supported options is individual for each node.
Script Node Slots
The script node is derived from the Process node.
| Slot Name | Slot Type | Data Type | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In | Out | ||||||
| Arguments | x |  | |||||
| BaseDir | x |  | Base directory | ||||
| Command | x |  | Executing Command | ||||
| Content | x |  | Content of the script file | ||||
| Design | x |  | Receiving design | ||||
| Environment | x |  | List of environment variables | ||||
| ErrorCode | x |  | Error code | ||||
| MaxParallel | x |  | Number of parallel runs | ||||
| MaxRuntime | x |  | Maximum runtime (in milliseconds) | ||||
| Starting Delay | x |  | Delay before a process is started | ||||
| WorkingDir | x |  | Path to working directory | ||||
| Design | x |  | Solved design | ||||
| ErrorCode | x |  | Error code | ||||
| MaxParallel | x |  | Number of parallel runs | ||||
| StdErr | x |  | Error text | ||||
| StdOut | x |  | Output text | ||||
| WorkingDir | x |  | Path to working directory | ||||
Supported Versions
See the Supported Integration Versions table.


