Table 5.2: Range of Application of Different Qualified Reliability Methods provides an overview of reliability algorithms implemented in optiSLang along with some recommendations for application.
Table 5.2: Range of Application of Different Qualified Reliability Methods
| Approach | Non-Linearity | Failure Domains | Number of Paramenters | Number of Solver Runs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monte Carlo SImulation | arbitrary | arbitrary | many |
>10^4 (3 sigma) >10^7 (5 sigma) |
| Directional Sampling | arbitrary | arbitrary | <= 10 | 1000-5000 |
| Adaptive Importance Sampling | arbitrary | one dominant | <= 10 | 500-1000 |
| FORM, SORM, ISPUD | monotonic | one dominant | <= 20 | 200-500 |
| Adaptive Response Surface Method | continuous | few dominant | <= 20 | 200-500 |
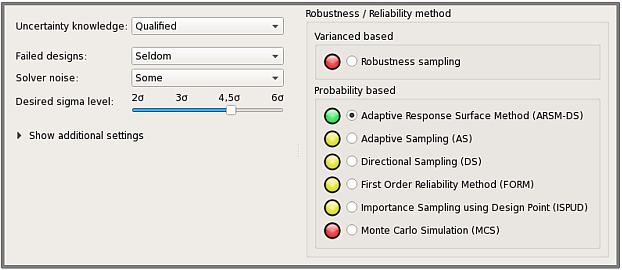
The robustness wizard in optiSLang helps with the decision of which method to choose. If the robustness analysis is set up with help of this wizard, there is a dialog in which some information has to be provided by the user as follows:
Uncertainty knowledge: Unaware | Estimated | Qualified
Failed designs: None | Seldom | Frequently
Solver noise: None | Some | Strong
Sigma level: Range
set by slider
The number of stochastic parameters and defined limit states is already known to the program. The response is given as a traffic light in the list of algorithms to choose from, see Figure 5.7: Dialog of the Robustness Wizard. The green color marks the recommended method, red is discouraged. A method marked yellow can be chosen by the experienced user, this should be done with care. If no limit state is defined and/or the uncertainty knowledge is unaware or estimated, then the recommendation is "Robustness sampling", i.e. a variance based robustness analysis.