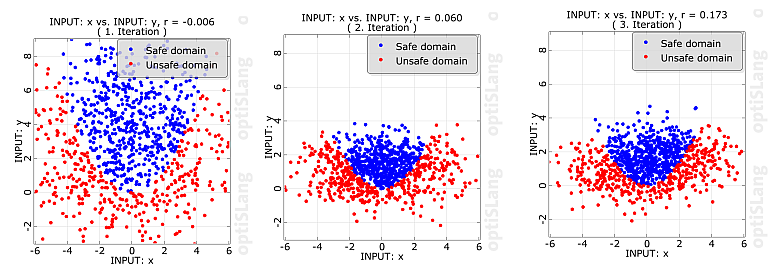
The ISPUD strategy (Bourgund and Bucher 1986) is to center the sampling density at the failure surface in the region of highest probability density. For this purpose, a searching procedure analogous to FORM (First Order Reliability Method (FORM)) is applied.
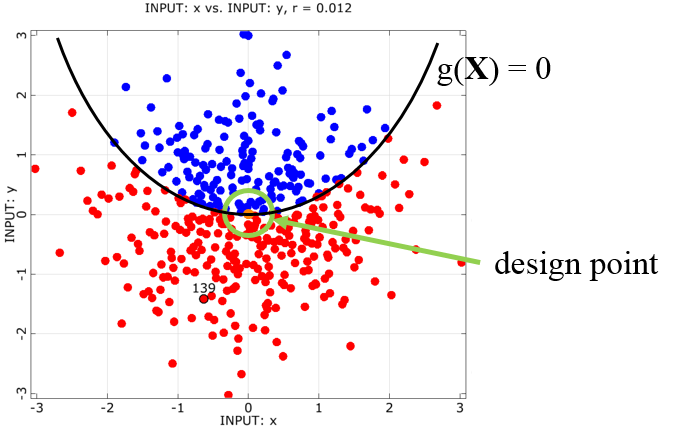
The sampling density h Y has a mean vector defined by the design point transformed back to original space. Distribution types, variances and correlations are taken over from the definitions of the original random parameters.
(5–22) |
(5–23) |
Figure 5.4: Parabola Example: Anthill Plot of Importance Sampling Using the Design Point shows the ISPUD sampling for the same example of a parabola, as it is introduced in Adaptive Sampling (ADSAP).
As for FORM, the success of the optimization step is crucial also for this method. At present, the gradient-based NLPQL algorithm is used, so the limit state function has to be sufficiently smooth, continuous, with a unique design point. If the design point can be determined correctly, ISPUD can overcome inaccuracies due to the linearization, which is typical for FORM.