VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-031
VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-031
Deflection of Beam using Symmetry and Anti-Symmetry
Overview
| Reference: | Any standard strength-of-materials book |
| Analysis Type(s): | Static Structural Analysis |
| Element Type(s): | Beam |
| Input Files: | Link to Input Files Download Page |
Test Case
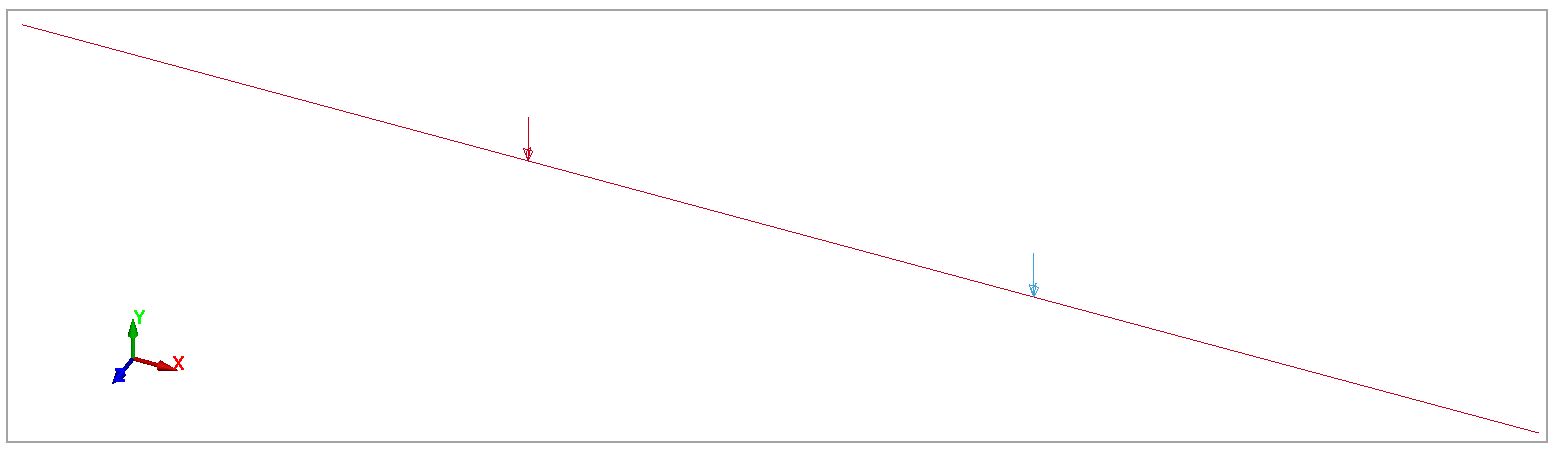
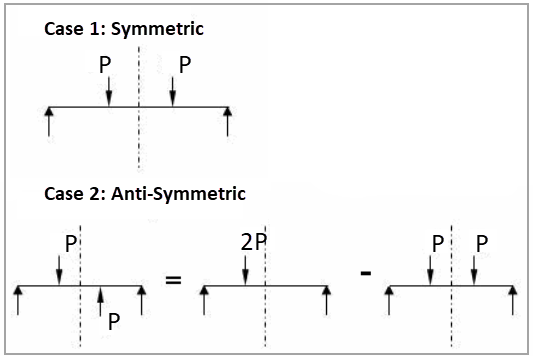
A long bar 1 m x 1 m x 24 m with simply supported ends is subjected to lateral load of 1000 N at a distance of 8 m from one end. Find the deformation in the Y direction at 8 m from the simply supported end. As shown in Figure 112, the study considers two cases: In the first test case, both loads act in the same direction (symmetric). In the second, one load acts in one direction along the Y-axis, and the other load acts in the opposite direction (antisymmetric). Figure 112 shows the external forces and supports for each case.
This test case also appears in the Workbench Verification Manual. See VM-WB-MECH-040.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
|
E = 2e11 Pa γ = 0 ρ = 0.001 kg/m3 |
Bar = 1 m x 1 m x 24 m |
Case 1 Symmetric: Force 1 = -1000 N (Y-direction) at 8 m from simply supported end Force 2 = -1000 N (Y-direction) at 16 m from simply supported end
Case 2 Anti-Symmetric: Force 1 = -1000 N (Y-direction) at 8 m from simply supported end Force 2 = 1000 N (Y-direction) at 16 m from simply supported end |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
For case 1, considering symmetry, the following formula is used for the displacement in the Y-direction:
(1) |
For case 2, considering anti-symmetry, the following formula is used for the displacement in the Y-direction:
(2) |
where
In LS-DYNA, a beam-type model (using the SECTION_BEAM keyword) is used by selecting the section type with a value for ELFORM of 1 (using the Hughes-Liu formulation with cross-section integration) and a value for QR/IRID of 2 (2 x 2 Gauss quadrature). As shown in the figures below, the mesh has been divided for each of the cases.