VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-017
VM-LSDYNA-SOLVE-017
3D Tension Failure Test (Cubes)
Overview
| Reference: | Any solid mechanics textbook |
| Analysis Type(s): | Explicit Dynamics 3D |
| Element Type(s): | Solid, Hexahedral and Tetrahedral Elements |
| Input Files: | Link to Input Files Download Page |
Test Case
This test case also appears in the Explicit Dynamics Verification Manual. See VM-EXD-MECH-005.
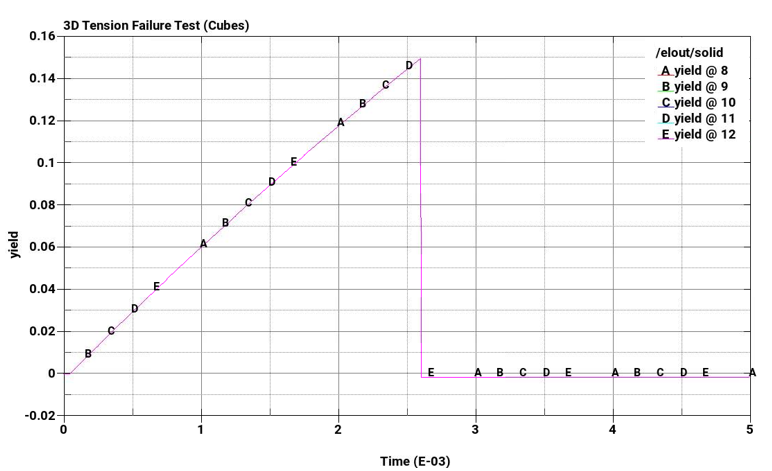
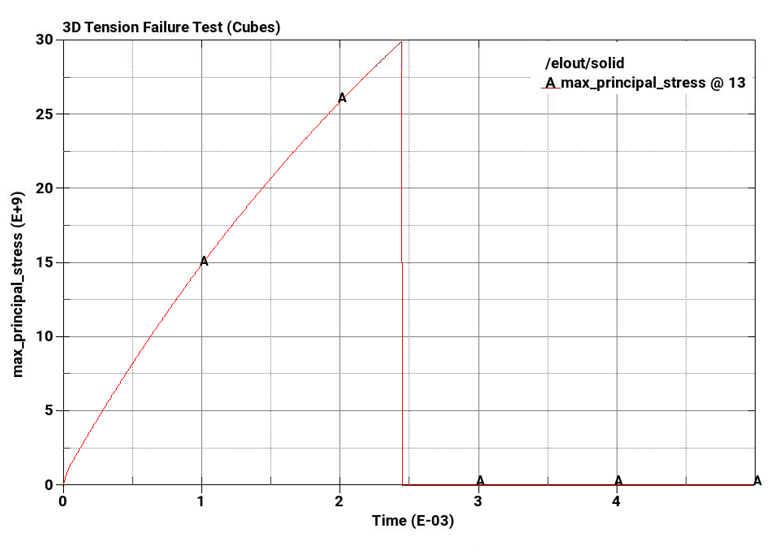
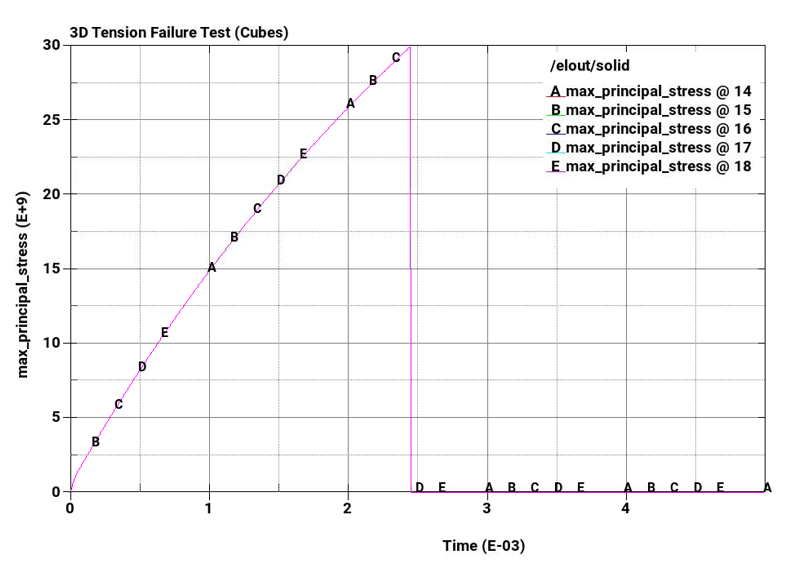
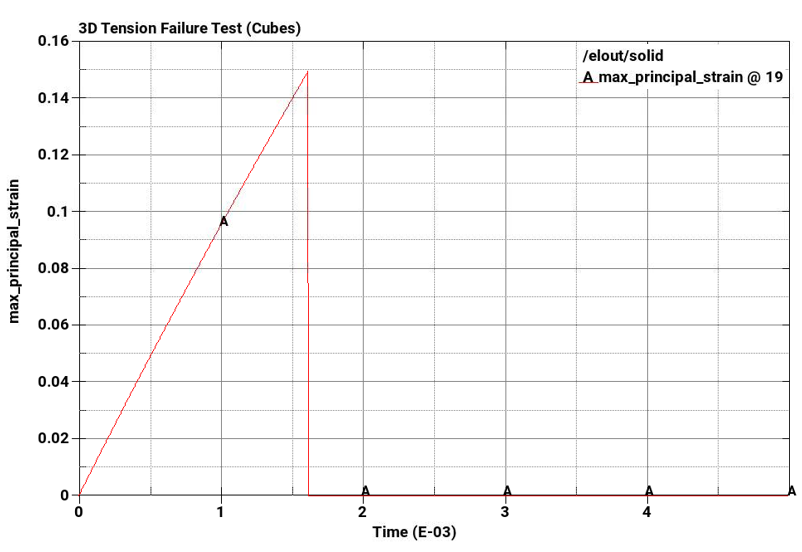
The problem tests the tensile pressure failure, plastic strain failure, principal stress failure, and principal strain failure of 8-node linear interpolated reduced integration constant stress hexahedral elements and reduced integration tetrahedral elements subjected to pure tension.
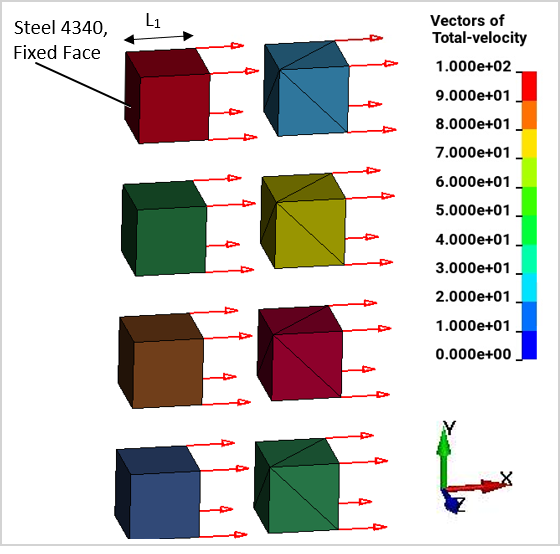
Four hex-part/tet-part pairs are each assigned a different material. All four materials use Steel 4340, but with different failure criteria. From top to bottom, the failure criteria are:
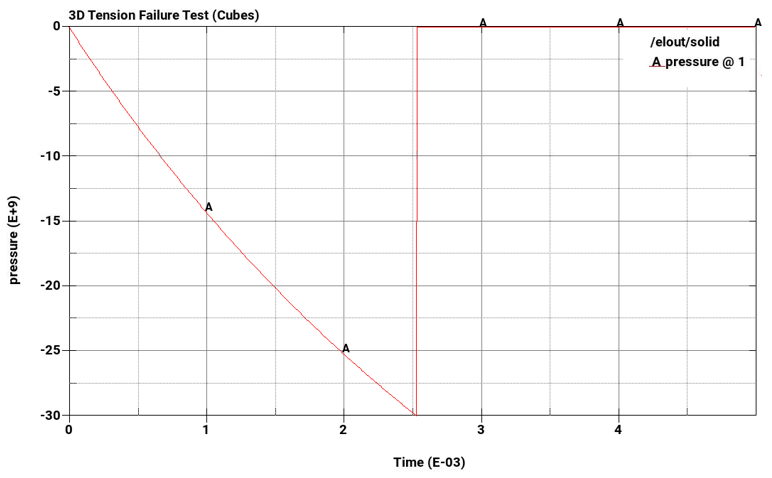
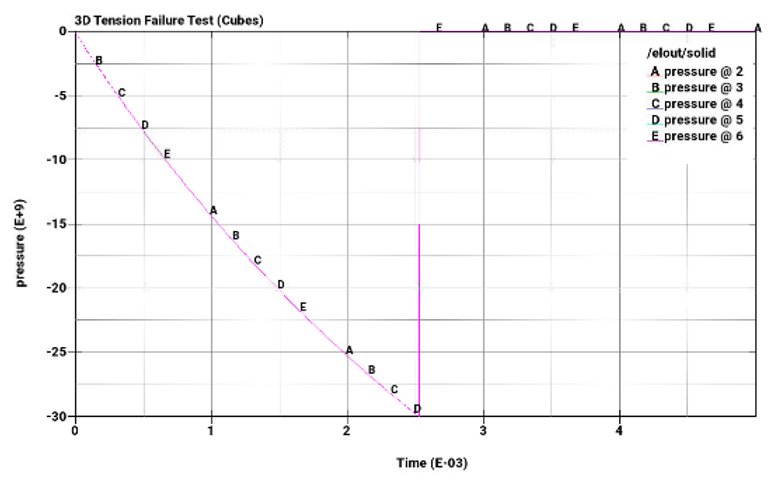
Tensile pressure failure at a maximum tensile pressure = -3E+10 Pa
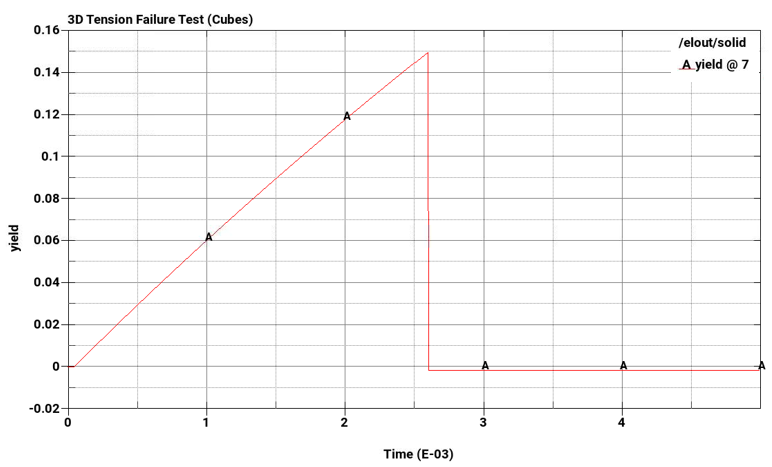
Plastic strain failure at strain = 0.15
Principal stress failure at a maximum principal stress = 3E+10Pa
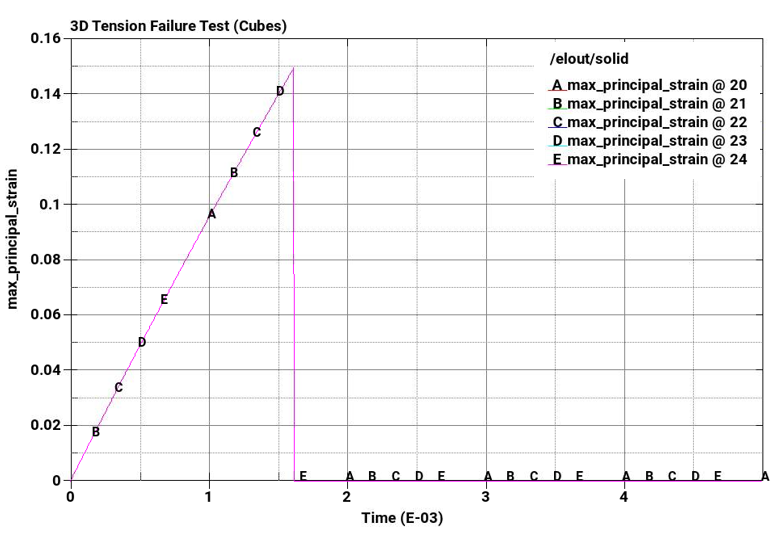
Principal strain failure at a maximum principal strain = 0.15
The left boundary of each cube has a fixed constraint. The right boundary of each cube is constrained to translation in the x-direction. A constant x-velocity of 100 m/s is applied to the right boundary of each cube. The calculation is run with a fixed time step of 5E–6 s for 1000 cycles.
Plot element pressure, effective plastic strain, principal stress, and principal strain vs. time for the pairs of cubes from top to bottom.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
| E = 2.07E11 Pa | L1 = L2 = L3 = L4 = 1m | vr = 100m/s |
| v = 0.29 | – | – |
| σyield = 7.10E8 Pa | – | – |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The load curve LCTM in *CONTROL_TIMESTEP defines a constant timestep of 5E-6s. Hex elements use ELFORM 1, while tets use ELFORM 10. *DATABASE_ELOUT, *DATABASE_EXTENET_BINARY, and *DATABASE_HISTORY_SOLID_SET were used to monitor element stresses and strain.
Steel 4340 material properties were defined using *MAT_PLASTIC_KINEMATIC. Failure Criteria for each hex and tet set were defined in *MAT_ADD_EROSION. *BOUNDARY_SPC_SET was used to define boundary constraints on the left and right faces of the cubes. *BOUNDARY_PRESCIRBED_MOTION, with DOF = 1, VAD = 0, and LCID as time history of velocity describes the x-velocity on the right face of each cube.
Results Comparison
The following plots show pressure, effective plastic strain, principal stress, and principal strain vs. time for the pairs of cubes from top to bottom. The A-plots are of hex elements, while the B-plots are of tet elements. Stress and strain drop to zero on element failure due to *MAT_ADD_EROSION, which causes the elements to erode once failure criteria is met. In all cases, the failure points correspond to the defined failure limits.