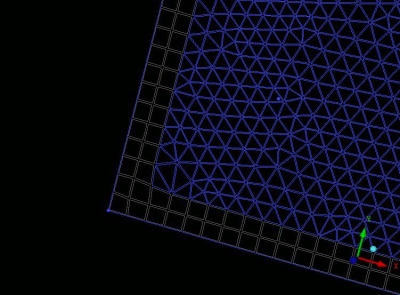
Only one element type can be remeshed at a time. Select a particular surface mesh type from the Mesh type drop-down list and then manually select particular elements. The selected elements are first deleted, and then the vacant area is remeshed. The element sizes are determined by the size of the surrounding edges.
Only one element type can be remeshed at a time. Select a particular surface mesh type from the Mesh type drop-down list and then manually select particular elements. The selected elements are first deleted, and then the vacant area is remeshed. The element sizes are determined by the size of the surrounding edges.
Note: This option is designed for plane subsets of the surface mesh, and for selected volume parts, but not for curved surfaces or entire volumes.
Tip: To speed the mesh refinement, turn off visibility of in the Display Tree before applying the remesh.
- Part
The remeshed elements will be added to the selected part.
- Surface projection
allows you to project new nodes onto the nearest surface.
- Ignore projection
if enabled, projections to curves and points will be ignored when remeshing. If a group of elements that are being remeshed have internal nodes that are projected to curves or points, and if Ignore projection is disabled, the elements will not be able to be remeshed as the projections will be lost.
- Number of offset layers
specifies the total number of offset layers while remeshing the selected elements.
- Offset height factor
The height of the first offset layer is this factor multiplied by the given element size. The height of any successive layers will increase for concave edges, and decrease for convex edges.
- Offset type
Standard
Offsets will be created normal to the edges without special solutions for sections with small or large angles, such as corners. The number of nodes on the offset front may not be identical as the number of nodes on the initial boundary.
Simple
Offsets will be created normal to the edges without special solutions for sections with small or large angles, such as corners. The number of nodes on the offset front is identical to the number of nodes on the initial boundary.
Forced Simple
This option is the same as Simple Offset, but without collision checking.