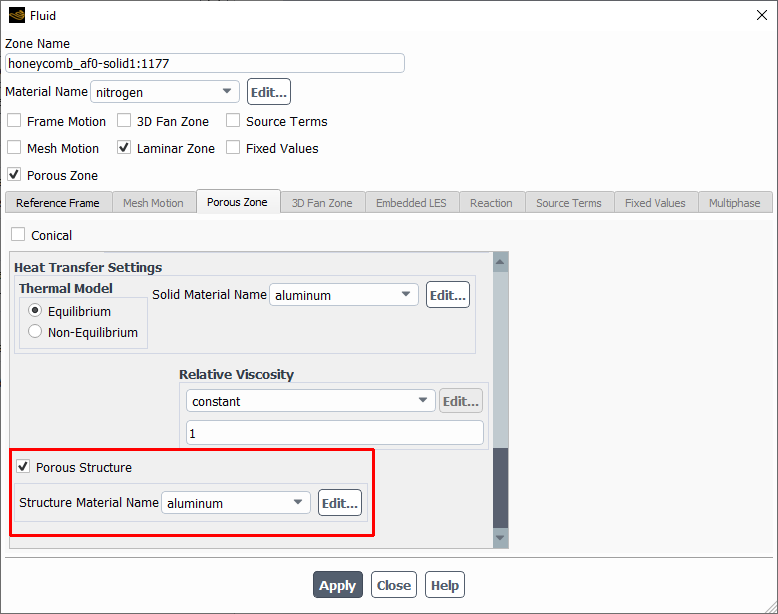
The structural model allows you to calculate deformation of porous structures. To set up such a simulation, enable beta feature access (as described in Introduction). Once beta features are enabled, for every porous zone that you intend to consider as a porous structure, select the Porous Structure option within the Porous Zone tab for the corresponding porous zone(s).
Once the Porous Structure option is enabled, select the Structure Material Name to be used within the porous structure. All porous zones that are declared as porous structures will be added to the overall list of zones on which the structural model is intended to be applied. All porous structures must be enabled up-front (similarly to how solid zones are available up-front) before the general structural model is enabled. This will allow Fluent to determine whether the case set up contains any incompatibilities relevant for the structural model.
The porous structure feature can also be enabled using either of the text user interface (TUI) commands:
/define/boundary-conditions/fluid
/define/boundary-conditions/fluid/set/fluid
Refer to the following sections for details about the theoretical basis of the porous structure model:
The constitutive equations that are used by the structural model for solid zones are equally applicable to porous structures as well, however, care is required when defining and selecting structural materials within the porous structure. Such material must take into account the level of porosity (or any other relevant properties) that may be present within the porous material.
As with solid zones, the boundary conditions for porous structures are available at free walls as well as at coupled walls between the fluid and solid zones. Additionally, structural boundary conditions can be applied to many other zones that may surround the porous structure, including, velocity-inlet, pressure-inlet, pressure-outlet, mass-flow inlet, mass-flow outlet, outflow, and pressure-far-field. For boundaries between fluid and porous-structure zones, the structural boundary conditions can also be set to a porous jump.