The structural model allows you to model linear elasticity for orthotropic materials. To set up such a simulation, enable beta feature access (as described in Introduction), select the appropriate orthotropic materials and their properties, and proceed as usual in setting up your structural analysis as described by Modeling Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) Within Fluent.
Note: Orthotropic materials are only available for the Linear Elasticity structural model.
The following sections contain details about the theoretical basis of the orthotropic materials structural analysis, and accessing their material properties.
In the context of orthotropic linear elasticity, the constitutive equations for all six stresses (including thermal effects) for 3D are given by:
(17–1) |
|
where | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
For orthotropic materials, you need to provide the correct values of the shear moduli (as described in Orthotropic Material Properties) since default values are zero.
Orthotropic materials require that you provide accurate values for the Young's modulus,
Poisson's ratio, and the thermal expansion coefficient. Note that Orthotropic Youngs
Modulus, Orthotropic Poisson Ratio, and Orthotropic
Thermal Expansion can also be defined using a user-defined function (UDF) by
interpreting or compiling a suitable UDF. For details, see
DEFINE_PROPERTY UDFs in the Fluent Customization Manual.
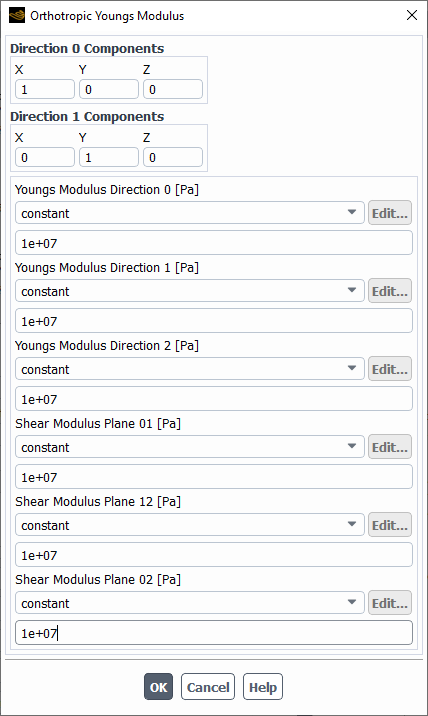
To provide an accurate value for the Young's modulus in the x, y, and z coordinate direction, select the orthotropic-structure-ym option for the Youngs Modulus field in the Create/Edit Materials dialog. This will open the Orthotropic Youngs Modulus dialog.
In the Orthotropic Youngs Modulus dialog, you can specify the direction components for material coordinates. The default values assume that the material coordinate system coincides with the general solution coordinate system. If the material coordinate system is rotated when compared to the general coordinate system, you will need to adjust the Direction 0 Components and/or the Direction 1 Components fields. Since the system is orthotropic, in 3D, you need to provide the Direction 0 and Direction 1 specifications, while, in 2D, you only need to specify Direction 0.
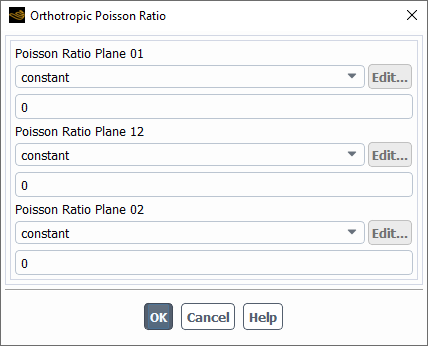
Likewise, to provide the Poisson ratio values in the xy, xz and yz planes, select the orthotropic-structure-nu option for the Poisson Ratio field in the Create/Edit Materials dialog..
This will open the Orthotropic Poisson Ratio dialog.
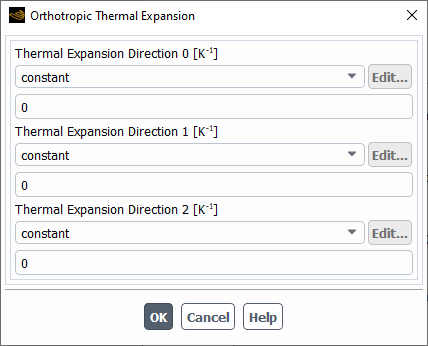
Similarly, when thermal effects are considered in the structural analysis, specify the thermal expansion coefficient by selecting the orthotropic-structure-te option for the Thermal Expansion field in the Create/Edit Materials dialog.
This will open the Orthotropic Thermal Expansion dialog.
Note: The same material Direction 0 Components and/or Direction 1 Components that you specify in the Orthotropic Youngs Modulus dialog are also used by the dialogs for the Orthotropic Poisson ratio and the Orthotropic Thermal Expansion Coefficient dialog.