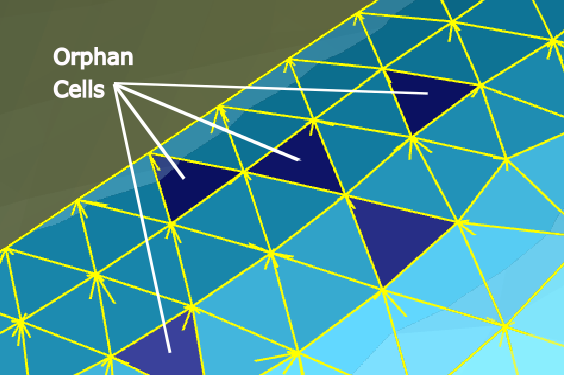
Occasionally, creating overlapping overset meshes creates mismatched cells, or orphan cells. The presence of orphan cells generally indicates that there is insufficient overlap between meshes or that the mesh resolutions do not match well. See Overset Meshes for more information.
Use the Identify Orphans task to identify any orphan cells In selected overset meshed.
Select one or more mesh objects from the list.
Select items in the list, or use the Filter Text option in the drop-down to provide text and/or regular expressions in filtering the list (for example, using *, ?, and []). You can also choose the Use Wildcard option in the drop-down to provide wildcard expressions in filtering the list. When you use either
?or*in your expression, the matching list item(s) are automatically selected in the list. Use^,|, and&in your expression to indicate boolean operations for NOT, OR, and AND, respectively. See Filtering Lists and Using Wildcards for more information.Choose a Donor Priority Method, that will control the location of the overset mesh. See Overset Domain Connectivity for more details about orphans, donors, and receptors in overset meshes.
Select Cell Volume Based to ensure the donor priority is based on the cell size (proportional to the inverse of the cell volume)
Select Boundary Distance Based to ensure the donor priority is based on the boundary distance (proportional to the inverse of the distance to the closest boundary)
For the Overlap Boundaries? option, determine if you need to account for any overlapping boundaries that may be present in your overset mesh (due to overlapping geometry and boundaries or those sometimes generated by collar meshes). You can improve the overset performance by setting this option to no.
Use the Enable Grid Priorities check box to turn on/off the ability to prioritize your overset meshes, or grids. When this option is turned on, a table of overset grids are presented where you can view their Names and edit their Grid Priority settings directly in the table. By default, all component meshes are given the same priority of 0. You can assign a higher value to increase the prioritization of a particular component mesh. The overset grid priorities are then carried over into the Fluent solver, and can be confirmed using the
define/overset-interface/grid-prioritiescommand.Use the Check Overset Interface Intersection option, enabled by default, to check for any intersections in your overset interfaces while identifying orphans. If you want to skip the check for intersections, then disabling this option increases the speed of identifying orphans.
Indicate the Number of Orphans.
Once your selection is made, click Identify Orphans to visualize orphan cells in the graphics window.
You can visualize orphan cells, as well as solve and receptor cells using the Show Orphan Cells, Show Solve Cells, or Show Receptor Cells buttons respectively. These options can also be used in conjunction with the visualization of the clipping plane via the ribbon.
If you need to make adjustments to any of your settings in this task, click Revert and Edit, make your changes and click Update, or click Cancel to cancel your changes.