VMFL026
VMFL026
Supersonic
Flow with Real Gas Effects inside a Shock Tube
Overview
| Reference | K. Mohamed, M. Paraschivoiu, “Real Gas Numerical Simulation of Hydrogen Flow”. 2nd International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, Providence, Rhode Island, Aug. 16-19, 2004 | |
| Solver | Ansys Fluent | |
| Physics/Models | Transient Compressible flow, Real Gas effects, Shock | |
| Input File |
| |
| Project Files | Link to Project Files Download Page |
Test Case
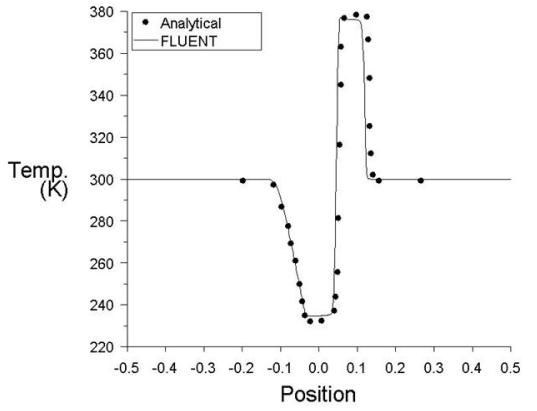
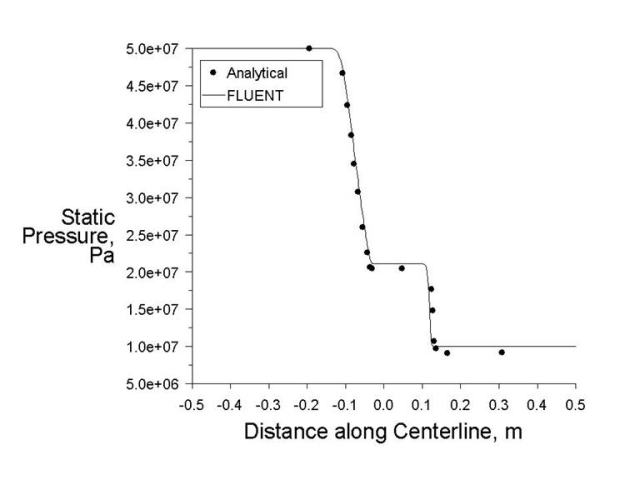
Transient flow inside a hydrogen filled shock tube is modeled. A diaphragm separating regions of high and low pressures ruptures at t = 0 thereby creating a shock wave in the tube.
Table 25: Materials, Geometry, and Boundary Conditions
| Material Properties | Geometry | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
|
Density is specified using the Aungier-Redlich-Kwong real gas model |
Length of the tube = 1 m Area of cross section = 0.01 m2 |
Cell zone conditions are specified with high pressure and low pressure properties of hydrogen |