Start Up
Starting EnSight RLSOS requires the use of EnShell to launch all processes
and properly configure them. Review the Cave Environment, Wall Displays & Head-mounted Displays documentation for
configuration instructions. Typically, someone at a site configures one or more EnShell networks
for the site while most EnSight users simply use these locally configured EnShell networks. You
typically access the EnShell networks and launch EnSight via the -based program
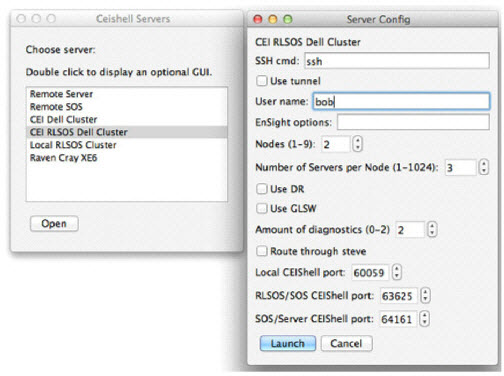
ceistart (see the figure for an example configuration).
In terms of configuring a EnShell network for use with RLSOS and optionally EnSight Enterprise (formerly HPC+), the concepts are exactly the same as with configuring any EnShell network. The sole exceptions are specifying the EnShell role tags RLSOS and multiple SOS roles to the appropriate EnShells. Figure : Simple RLSOS Connectivity shows a typical EnShell network layout. One EnShell has the role RLSOS, one or more child EnShells have the role "SOS", and each of the SOS EnShells have one or more child EnShells with the role SOS_SERVERS. In the example represented by the figure, EnSight will start and use via this EnShell network one RLSOS, two SOSes, and six Servers.
If EnSight Enterprise (formerly HPC+) is to be used with RLSOS, then the computer executing the RLSOS must be able to open a network connection to the computer(s) running the EnSight CollabHub as well as the EnSight master Client. Additionally, the EnSight Enterprise (formerly HPC+) Clients must be able to open network connections to the EnSight CollabHub and master Client. A future version of EnSight and EnShell may provide for network tunneling via EnShell.
Operation
To the end-user of EnSight, once RLSOS is running, there is no other difference from using RLSOS compared to using EnSight with just SOS -- all user interaction is the same as it is with SOS use.
Limitations
Currently, the only known limitation when using RLSOS concerns the use of legacy EnSight SOS Case files (not normal Case files). If a legacy SOS Case file is used, then it must not contain 'machine id:' nor 'executable: lines. Additionally, the 'number of servers: in the SOS Case file must match the total number of EnSight Servers started by the EnShell network. Lastly, the underlying data files specified in the SOS Case file must be accessible by all Servers since it is not known apriori which Server will read which data file.
Multiple Case File (MCF) Interface
When running EnSight in parallel (either SOS or RLSOS), the steps for you
to load spatially decomposed Case Gold datasets is the same as when running non-parallel.
EnSight Enterprise (formerly HPC or Gold) automatically handles the assignment of the multiple
Case Gold datasets to Servers, whether they are selected interactively using the Data Reader
dialog MCF interface (see Reader Basics ), or using the EnSight_MCF reader with one .mcf file
(see Multiple Case File Format). EnSight will round-robin the assignment of datasets
to Servers as long as there is at least one Case Gold dataset for every server.
Note: All of the Case Gold datasets specified in the Multiple Case File must be readable by all Servers since it is not known in advance which Server will read which dataset.
Creation of the MCF file prior to the EnSight RLSOS, and avoiding the use of wildcards in the MCF will allow all the Servers to simply read the filenames from the MCF file. This can avoid the pitfall of having a large number of Servers taxing the operating system and the file system attempting to resolve a large number of Case Gold filenames from wildcards.