This section lists symbols used in this chapter, together with their meanings, dimensions and where applicable, values. Dimensionless quantities are denoted by 1. The values of physical constants (or their default values) are also given.
More information on the notation used in the multiphase and multicomponent chapters is available:
Symbol
Description
Dimensions
Value
linear energy source coefficient
linear resistance coefficient
quadratic resistance coefficient
-
turbulence model constant
RNG
-
turbulence model coefficient
-
turbulence model constant
RNG
-
turbulence model constant
-
turbulence model constant
Reynolds Stress model constant
RNG
-
turbulence model constant
fluid speed of sound
concentration of components A and B (that is, mass per unit volume of components A and B (single-phase flow))
Reynolds Stress model constant
specific heat capacity at constant pressure
specific heat capacity at constant volume
Reynolds Stress model constant
Reynolds Stress model constant
binary diffusivity of component A in component B
kinematic diffusivity of an Additional Variable,
distance or length
constant used for near-wall modeling
Zero Equation turbulence model constant
RNG-
-
turbulence model coefficient
gravity vector
specific static (thermodynamic) enthalpy
For details, see Static Enthalpy.
Hartmann Number: the ratio of the Lorentz forces to the viscous forces.
heat transfer coefficient
specific total enthalpy
For details, see Total Enthalpy.
turbulence kinetic energy per unit mass
local Mach number,
mass flow rate
shear production of turbulence
static (thermodynamic) pressure
For details, see Static Pressure.
reference pressure
For details, see Reference Pressure.
total pressure
For details, see Total Pressure.
modified pressure
For details, see Modified Pressure.
universal gas constant
Reynolds number,
Magnetic Reynolds Number: the ratio between the magnetic advection and magnetic diffusion.
location vector
volume fraction of phase
energy source
momentum source
mass source
turbulent Schmidt number,
Stanton number mass flow rate from phase
to phase
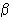 .
.static (thermodynamic) temperature
For details, see Static Temperature.
domain temperature
For details, see Domain Temperature.
buoyancy reference temperature used in the Boussinesq approximation
saturation temperature
total temperature
For details, see Total Temperature.
vector of velocity
velocity magnitude
fluctuating velocity component in turbulent flow
fluid viscous and body force work term
molecular weight (Ideal Gas fluid model)
mass fraction of component A in the fluid
used as a subscript to indicate that the quantity applies to phase
used as a subscript to indicate that the quantity applies to phase
coefficient of thermal expansion (for the Boussinesq approximation)
RNG
-
turbulence model constant
diffusivity
molecular diffusion coefficient of component
turbulent diffusivity
turbulence dissipation rate
bulk viscosity
thermal conductivity
molecular (dynamic) viscosity
magnetic permeability
turbulent viscosity
effective viscosity,
density
laminar Prandtl number,
turbulent Prandtl number,
electrical conductivity
turbulence model constant for the
equation
-
turbulence model constant
-
turbulence model constant
Reynolds Stress model constant
RNG
-
turbulence model constant
RNG
-
turbulence model constant
shear stress or sub-grid scale stress
molecular stress tensor
specific volume
Additional Variable (non-reacting scalar)
general scalar variable
angular velocity
Quantities that appear with subscripts ,
,
refer to
that quantity for component
,
,
in a multicomponent
fluid.
Quantities that appear with subscripts ,
,
refer
to that quantity for phase
,
,
in
a multiphase flow.
Such quantities are used only in the chapters describing multicomponent and multiphase flows.


