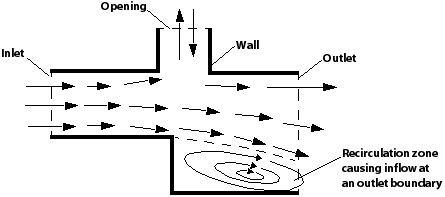
A fluid boundary is an external surface of a fluid domain and supports following boundary conditions:
Inlet- Fluid predominantly* flows into the domain.Outlet- Fluid predominantly* flows out of the domain.Opening- Fluid can simultaneously flow both in and out of the domain. This is not available for domain with more than one fluid present.Wall- Impenetrable boundary to fluid flow.Symmetry Plane- A plane of both geometric and flow symmetry.
* When you define an area to be an "inlet," you are telling CFX-Solver that you anticipate that flow will be into a domain. You can set either velocity or pressure at that point, and CFX-Solver will calculate the other value. How CFX-Solver behaves during the flow calculations depends on which attribute you set:
CFX-Solver allows both inflow and outflow due to the velocity specified conditions. "artificial walls" are not erected at inlets or outlets due to such conditions.
If you set pressure at an inlet, you may accidentally create conditions that would lead to an outflow when the pressure inside the domain is greater than outside. Under this condition, CFX-Solver "builds" an artificial wall to prevent outflow. To disable this behavior, define the boundary to be an "opening" rather than an inlet.
For details, see Using Inlets, Outlets and Openings.


