VM290
VM290
Pressurized Spherical Cavity in an Infinite Medium Using
Infinite Elements
Overview
| Reference: | Marques, J.M.M.C., Owen, D.R.J, “Infinite Elements in Quasi-Static Materially Nonlinear Problems,” Computers & Structures, Vol 18, No. 4, pp 739-751, 1984. |
| Analysis Type(s): | Static Analysis (ANTYPE = 0) |
| Element Type(s): |
Structural Infinite Solid (INFIN257) 3D 20-Node Structural Solid (SOLID186) |
| Input Listing: |
vm290.dat
VM290 requires a supplemental .cdb input file which is too long to include full input listings. This file must be downloaded and placed in your working directory for the test case to run properly. Additionally, the geometry and mesh should be regenerated. Download link: MAPDL Test Case Files for 2024 R2 vm290.cdb |
Test Case
A spherical cavity with a radius of 1.0 m is placed in an infinite medium. The spherical cavity is subjected to an internal pressure of 750 Pa. Structural semi-infinite solid elements are used to model the infinite domain. Determine the radial displacements with respect to location.
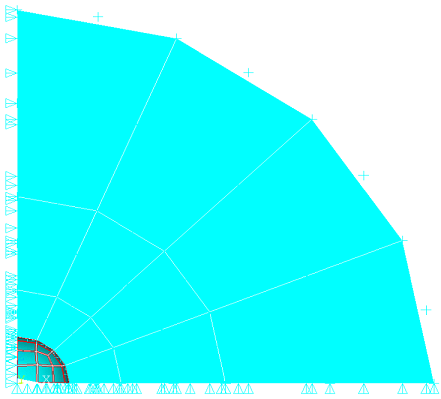
Figure 505: Finite/Infinite Element Mesh of a Pressurized Spherical Cavity in an Infinite Medium (SOLID186 and INFIN257)
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Young's modulus:
Poisson’s ratio:
| Internal radius:
| Internal pressure = 750 Pa |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
A spherical cavity is modeled using SOLID186 elements and the infinite medium is modeled using INFIN257 elements using the EINFIN command. Only one eighth of the sphere is modeled, using symmetric constraints on the three orthogonal planes. The displacements along the radial direction are then obtained from /POST1 and compared against the reference results provided in the Results Comparison table.
The analytic solution for radial displacement is:
The analytic solution for radial stress is:
The analytic solution for tangential stress is:
where is the internal applied pressure,
is the internal
radius,
is the rigidity modulus, and
is the radial
location.


