VM260
VM260
Two-Dimensional Consolidation Settlement Problem
Overview
Test Case
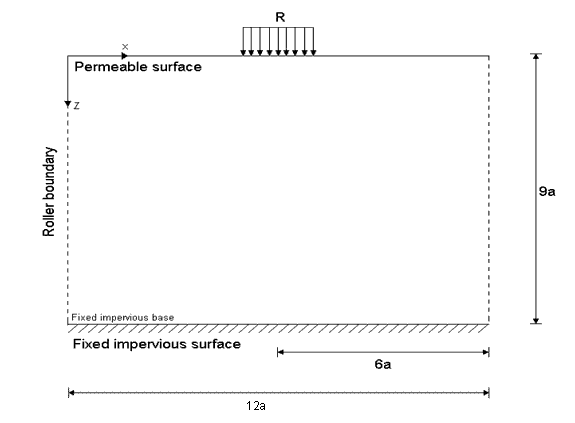
An infinite rectangular half space plate is modeled with dimensions 12a by 9a. Pressure loading is applied on the center of the top surface (on one sixth of the total width). The top surface is made permeable and bottom surface is impermeable. Evolution of pore pressure computed with respect to depth and time are compared with reference values.
Nomenclature Used in This Problem
| P = Pore pressure |
| Tv =
|
| Tv = Time Factor |
| CVc = Consolidation coefficient |
| t = Time |
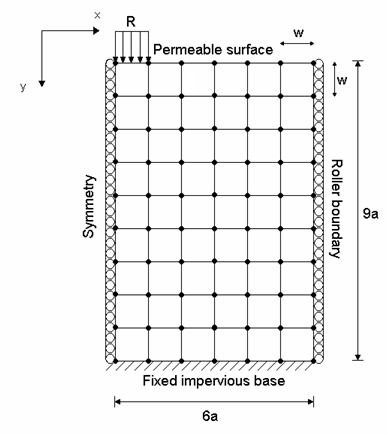
Figure 448: Two-Dimensional Consolidation Pore-Pressure Problem -- Representative Finite Element Model
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The plate is meshed using (CPT212) and (CPT213) elements with plane strain conditions. Permeability and Biot coefficients are defined to the material model using TBDATA command. Bottom surface is fixed in all directions and displacements along X directions are constrained on the right and left edges. Non-linear static analysis is then performed to compute the evolution of pore pressure with respect to time and depth.
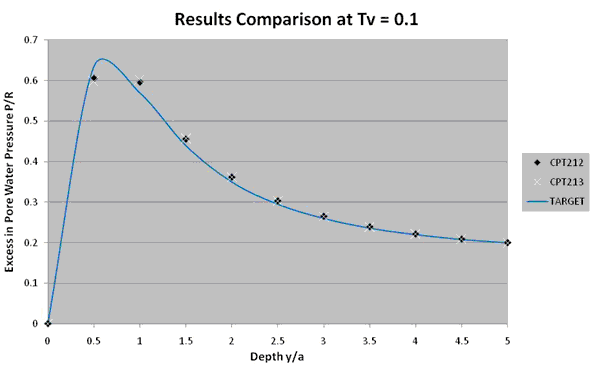
Results Comparison for the Evolution of P with Depth
P/R (CPT212) | za | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
| 0 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.000 | |
| 0.5 | 0.6350 | 0.6053 | 1.049 | |
| 1 | 0.5700 | 0.5962 | 0.956 | |
| 1.5 | 0.4400 | 0.4555 | 0.966 | |
| 2 | 0.3500 | 0.3615 | 0.968 | |
| 2.5 | 0.2950 | 0.3029 | 0.974 | |
| 3 | 0.2600 | 0.2648 | 0.982 | |
| 3.5 | 0.2360 | 0.2390 | 0.988 | |
| 4 | 0.2200 | 0.2211 | 0.995 | |
| 4.5 | 0.2080 | 0.2087 | 0.997 | |
| 5 | 0.2000 | 0.2000 | 1.000 |
P/R (CPT213) | za | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
| 0 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.000 | |
| 0.5 | 0.6350 | 0.5983 | 1.061 | |
| 1 | 0.5700 | 0.6031 | 0.945 | |
| 1.5 | 0.4400 | 0.4578 | 0.961 | |
| 2 | 0.3500 | 0.3625 | 0.965 | |
| 2.5 | 0.2950 | 0.3037 | 0.971 | |
| 3 | 0.2600 | 0.2653 | 0.980 | |
| 3.5 | 0.2360 | 0.2394 | 0.986 | |
| 4 | 0.2200 | 0.2214 | 0.994 | |
| 4.5 | 0.2080 | 0.2089 | 0.996 | |
| 5 | 0.2000 | 0.2001 | 0.999 |
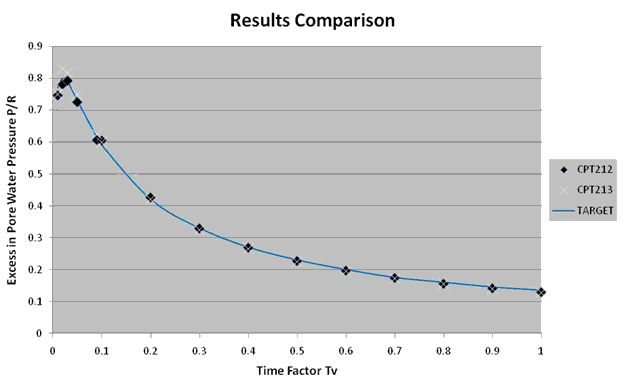
Results Comparison for the Evolution of P with Time
| P/R (CPT212) | Tv (za) | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
| 0.01 | 0.7700 | 0.7466 | 1.031 | |
| 0.02 | 0.8000 | 0.7812 | 1.024 | |
| 0.03 | 0.7900 | 0.7928 | 0.996 | |
| 0.05 | 0.7300 | 0.7257 | 1.006 | |
| 0.09 | 0.6150 | 0.6072 | 1.013 | |
| 0.1 | 0.5900 | 0.6053 | 0.975 | |
| 0.2 | 0.4200 | 0.4267 | 0.984 | |
| 0.3 | 0.3300 | 0.3294 | 1.002 | |
| 0.4 | 0.2700 | 0.2687 | 1.005 | |
| 0.5 | 0.2300 | 0.2271 | 1.013 | |
| 0.6 | 0.2000 | 0.1969 | 1.016 | |
| 0.7 | 0.1750 | 0.1739 | 1.006 | |
| 0.8 | 0.1600 | 0.1558 | 1.027 | |
| 0.9 | 0.1450 | 0.1412 | 1.027 | |
| 1.0 | 0.1350 | 0.1291 | 1.046 |
| P/R (CPT213) | Tv (za) | Target | Mechanical APDL | Ratio |
| 0.01 | 0.7700 | 0.7509 | 1.025 | |
| 0.02 | 0.8000 | 0.8298 | 0.964 | |
| 0.03 | 0.7900 | 0.8171 | 0.967 | |
| 0.05 | 0.7300 | 0.7497 | 0.974 | |
| 0.09 | 0.6150 | 0.6242 | 0.985 | |
| 0.1 | 0.5900 | 0.5983 | 0.986 | |
| 0.2 | 0.4200 | 0.4215 | 0.996 | |
| 0.3 | 0.3300 | 0.3258 | 1.013 | |
| 0.4 | 0.2700 | 0.2660 | 1.015 | |
| 0.5 | 0.2300 | 0.2251 | 1.022 | |
| 0.6 | 0.2000 | 0.1953 | 1.024 | |
| 0.7 | 0.1750 | 0.1725 | 1.014 | |
| 0.8 | 0.1600 | 0.1546 | 1.035 | |
| 0.9 | 0.1450 | 0.1402 | 1.034 | |
| 1.0 | 0.1350 | 0.1282 | 1.053 |