VM24
VM24
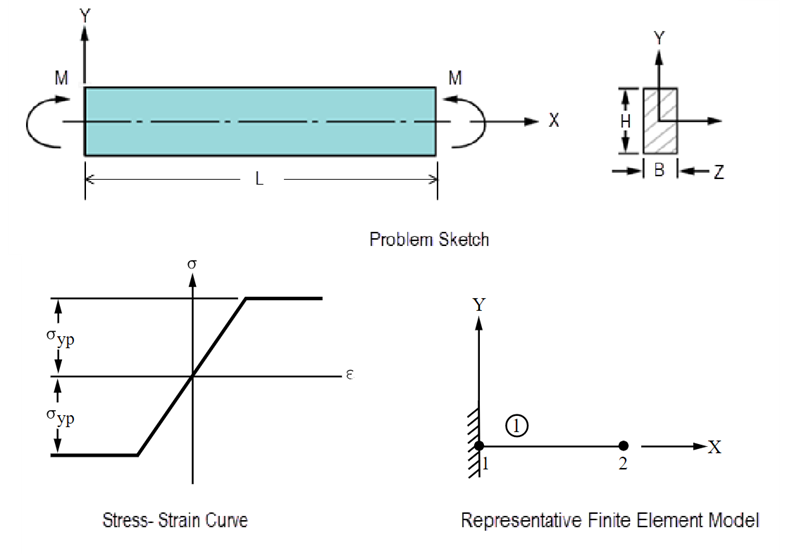
Plastic Hinge in a Rectangular Beam
Test Case
A rectangular beam is loaded in pure bending. For an elastic-perfectly-plastic stress-strain behavior, show that the beam remains elastic at M = Myp = σyp bh2/6 and becomes completely plastic at M = Mult = 1.5 Myp.
| Material Properties | Geometric Properties | Loading |
|---|---|---|
|
E = 30 x 106 psi ν = 0.3 σyp = 36000 psi |
B = 1 in H = 2 in L = 10in Iz = b h3/12 = 0.6667 in4 |
M = 1.0 Myp to 1.5 Myp (Myp = 24000 in-lb) |
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
Bilinear kinematic hardening (BKIN) and 6 cells are used through the thickness.
An arbitrary beam length is chosen. Because of symmetry, only half of the structure is modeled (since length is arbitrary, this means only that boundary conditions are changed). The load is applied in four increments using a do-loop, and convergence status is determined from the axial plastic strain for each load step in POST26.