VM173
VM173
Centerline Temperature of an Electrical Wire
Test Case
Determine the centerline temperature 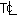 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R/I. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the
air (at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine
the heat dissipation rate q.
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R/I. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the
air (at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine
the heat dissipation rate q.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
A 1 inch axial (Z) length is chosen for convenience. Since
the problem is axisymmetric, only a one-element sector is needed.
A small angle Θ = 10° is used for approximating the
circular boundary with a straight-sided element.
The calculated resistivity, rho = RA/I, in units of [ohms-ft]
was converted to units of [(Btu/hr)/watt] using the conversion factor
[3.415 (ohm-ft)] / [(Btu/hr)/watt]. With this conversion, the Joule
heat units match the thermal units. The voltage drop per foot, IR/
 , is calculated as 0.1 volt/ft. Nodes 1 though
16 are assumed to be ground nodes for reference. The steady-state
convergence procedures are used. The heat dissipation rate, q, is
calculated as q = hA(T-Ta) where A = exterior
surface area of the wire (parameter AREA).
, is calculated as 0.1 volt/ft. Nodes 1 though
16 are assumed to be ground nodes for reference. The steady-state
convergence procedures are used. The heat dissipation rate, q, is
calculated as q = hA(T-Ta) where A = exterior
surface area of the wire (parameter AREA).
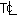 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R/I. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the
air (at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine
the heat dissipation rate q.
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire carrying a current I and having a resistance
R/I. The surface convection coefficient between the wire and the
air (at temperature Ta) is h. Also determine
the heat dissipation rate q., is calculated as 0.1 volt/ft. Nodes 1 though
16 are assumed to be ground nodes for reference. The steady-state
convergence procedures are used. The heat dissipation rate, q, is
calculated as q = hA(T-Ta) where A = exterior
surface area of the wire (parameter AREA).


