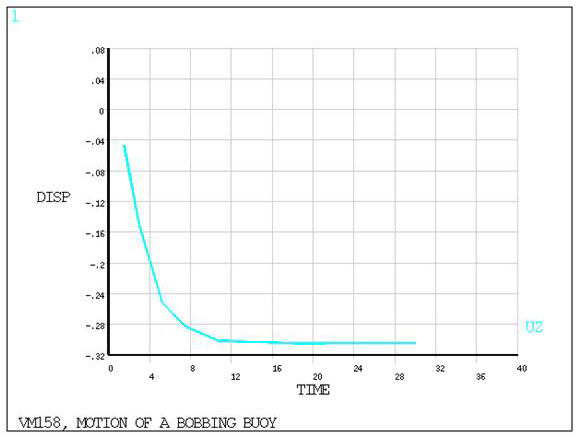
VM158
VM158
Motion of a Bobbing Buoy
Test Case
A cylindrical buoy is initially held at the position shown (above
its equilibrium position) and then released (with no initial velocity).
Determine the equilibrium position δ of the top of the
buoy relative to the water surface.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The static solution to this problem is best obtained by the "slow dynamics" technique with damping, since the buoy is initially
subjected to free fall. An arbitrary time to steady state of 30 sec
and 1.5 seconds per time step is selected for the slow dynamics.
The mass damping value α determines the bouncing (if any) before the final steady state solution.
An approximate α value
is determined from F/MV where the force F = CV and damping C = αM. The force F is the out-of-balance
force (buoyancy force
 minus
the buoy weight) for the initial position pushing the buoy into the
water, M is the mass of the buoy, and V is an estimated average velocity
(0.1 m/sec). Based upon these approximations, α
minus
the buoy weight) for the initial position pushing the buoy into the
water, M is the mass of the buoy, and V is an estimated average velocity
(0.1 m/sec). Based upon these approximations, α
 3 sec-1.
3 sec-1.
minus
the buoy weight) for the initial position pushing the buoy into the
water, M is the mass of the buoy, and V is an estimated average velocity
(0.1 m/sec). Based upon these approximations, α
3 sec-1.