VM118
VM118
Centerline Temperature of a Heat-generating Wire
Test Case
Determine the centerline temperature 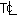 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire generating heat at the rate
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire generating heat at the rate
 . The surface convection coefficient between
the wire and the air (at temperature Ta) is
h. Also determine the heat dissipation rate q.
. The surface convection coefficient between
the wire and the air (at temperature Ta) is
h. Also determine the heat dissipation rate q.
Analysis Assumptions and Modeling Notes
The problem is solved first using conducting area elements
(PLANE55) and then using conducting solid
elements (SOLID70). Since the problem is
axisymmetric, only a one-element sector is needed. A small angle Θ
= 10° is used for approximating the circular boundary with a straight-sided
element. Nodal coupling is used to ensure circumferential symmetry.
The solution is based on a wire 1 foot long (Z-direction). POST1
is used to extract results from the solution phase. Total heat dissipation
is computed parametrically at the outer surface as HRATE using q =
h.area.(Ts - Ta).
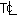 and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire generating heat at the rate
and the surface temperature Ts of a bare steel wire generating heat at the rate
. The surface convection coefficient between
the wire and the air (at temperature Ta) is
h. Also determine the heat dissipation rate q.


