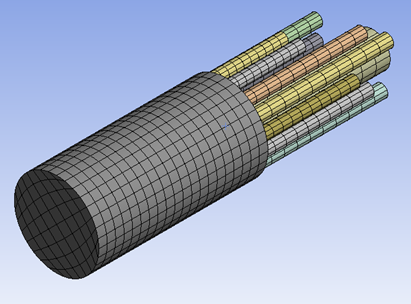
The 3D model of the structure is created in Ansys DesignModeler and meshed with FLUID220 and FLUID221 3D acoustic elements, with pressure as a unique degree of freedom (KEYOPT(2) = 1).
A normal velocity and a nonreflective radiation boundary are applied on the impedance tube inlet, simulating the sound generated experimentally by a speaker.
Boundary layer impedance (BLI) and low reduced frequency (LRF) models are successively applied on the resonator tubes to analyze viscous and thermal effects.
The element size chosen ensures at least six elements per wave length for the highest frequency of interest.
All bodies are grouped in a single part for node connectivity at the body’s interfaces.