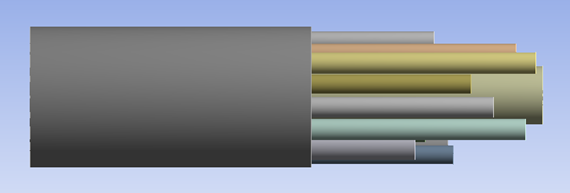
Development of systems for minimizing noise is an ongoing process, as noise is a factor that can quickly and adversely affect comfort. In an aircraft cabin, for example, the turbulent boundary layer surrounding the fuselage is a primary source of noise in the mid- to high-frequency range (500-2000 Hz). To reduce the sound pressure level in the cabin, an effective solution consists of quarter-wave resonator panels made of an assembly of tubes of varying diameters and lengths. The absorption capability of the resonator panel is the result of a combined effect of the quarter-wave phenomenon and viscothermal loss.
The problem presented here calculates the absorption coefficient of an example resonator panel.