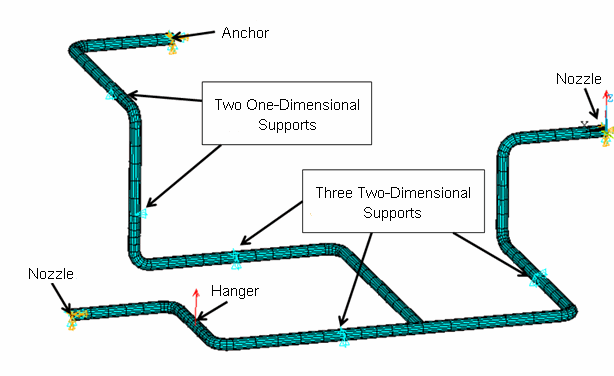
The problem involves a large-scale nuclear piping system consisting of straight pipes, nine elbows, and a tee:
Not shown in the figure is a 1000 kg mass representing a valve.
The system is supported by nozzles, an anchor, three two-directional supports, a horizontal support, a vertical support and a spring hanger.[1] The following analyses are performed on the piping system to study both global and local responses of the system when subjected to seismic loading:
Modal analysis of the entire piping system
Nonlinear static analysis of one of the critical elbows of the piping system using elbow element technology
Nonlinear static analysis of one of the critical elbows of the piping system using shell element technology