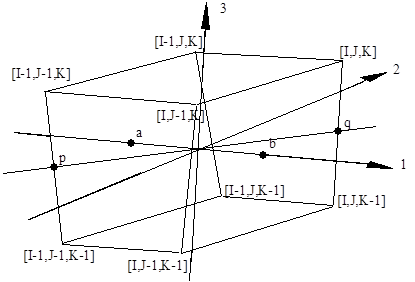
The first principal direction for each cell is relative to the direction of increasing I for each cell, as shown below. The directions are calculated individually for each cell when the material is filled into the cells; then the directions are stored as four variables exactly as for the X-Y-Z space option. The directions are found as follows:
The direction 1 is a vector from the centroid of the cell face I-1 (point a) to the centroid of cell face I (point b)
Next find the midpoints of the K-lines at [I-1,J-1] and [I,J], which are points p and q respectively
Direction 3 is the cross product of direction 1 and the vector through points p and q
Direction 2 is the cross product of directions 1 and 3
Using the I-J-K option you can define initial material directions that are aligned with the cells. This can be useful when modelling shapes such as cylinders where the principal directions are aligned with the major axes of the body.
Note: When the I-J-K Space option is selected for 3D unstructured Lagrange elements, the direction of the first principal axis will coincide with the global X-axis direction.