The Material Configuration section of the simulation form will change to include anisotropic coefficients if you have chosen a Scan Pattern or Thermal simulation type.
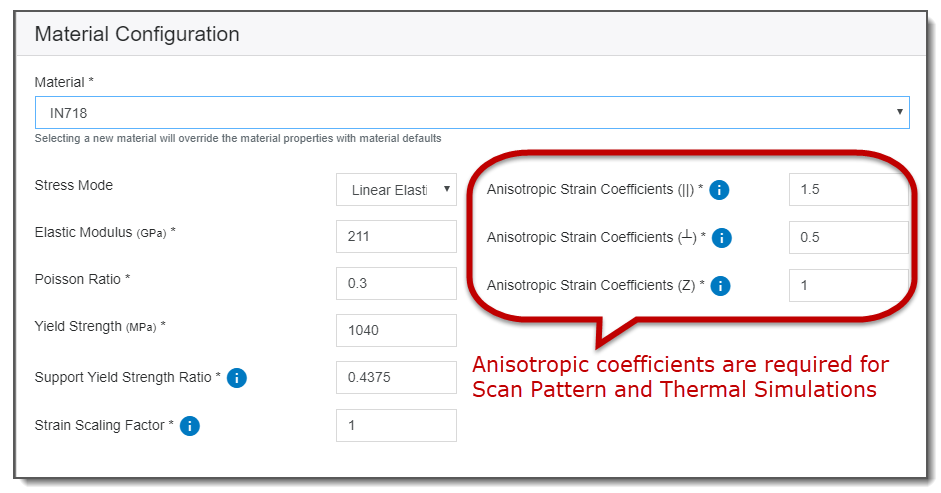
Anisotropic strain coefficients are used to represent anisotropic strain behavior on coordinate systems aligned with the local longitudinal, transverse, and depth scan directions. Positive values result in compressive base strain (contraction), whereas negative values result in tensile strain (expansion). Default values are shown in the following table.
|
Anisotropic strain coefficient (||) = 1.5 |
Longitudinal: The predicted strain in the direction that the laser is scanning for the major fill rasters will be multiplied by 1.5 |
|
Anisotropic strain coefficient (⊥) = 0.5 |
Transverse: The predicted strain orthogonal to the direction that the laser is scanning for the major fill rasters and in the plane of the surface of the build plate will be multiplied by 0.5 |
|
Anisotropic strain coefficient (z) = 1 |
Depth: The predicted strain in the Z direction will be multiplied by 1 |


