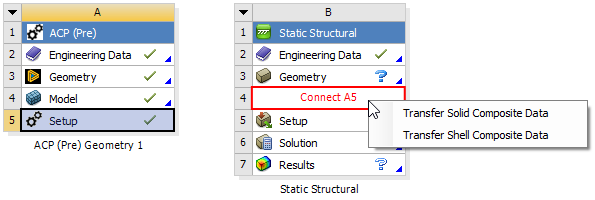
Similar to composite shells, composite solids defined using ACP can be imported into Mechanical for analysis by importing the mesh from upstream ACP systems and synthesizing the geometry from the imported meshes. The import of a composite solid from ACP into Mechanical follows the same procedure for shells except that the transfer option must be selected as shown below.
ACP distinguishes between two different approaches: the first approach is an extrusion algorithm that generates a solid mesh based on the Composite Definitions and the shell reference surface. This feature is simply called Solid Model. In this scenario the solid mesh is completely generated by ACP (Pre). For more information, refer to the Guide of Solid Modeling and the Analysis of a Composite Solid Model sections of the Help.
In the second approach, the Composite Definitions are mapped onto an external solid mesh that is loaded in ACP. This feature is called Imported Solid Model.
Load an External Solid Mesh in ACP (Pre)
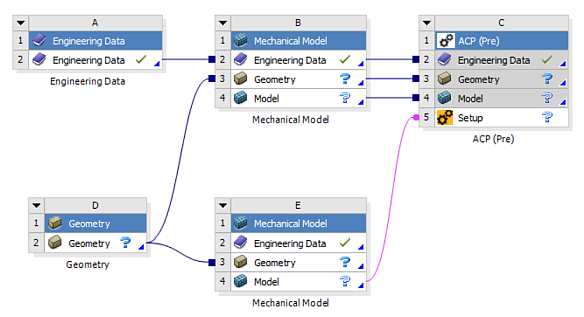
External solid meshes can be transferred to ACP (Pre) by linking a Mechanical Model component to ACP Setup as shown in the Figure below. This allows you to map the composite definitions onto the Imported Solid Model.
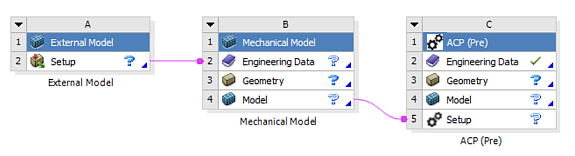
Solid meshes from third party applications can also be loaded into ACP (Pre). In that scenario the mesh is loaded via External Model and Mechanical Model as shown in the next figure.
Note: The internal link between the MechanicalModel and ACP Setup within an ACP (Pre) System (C4 to C5 in the figure above) transfers the shell mesh only.