In the case of thick composites, the layered shell theory can cause significant errors in the obtained results. In some cases, it is necessary to work with 3D models, also referred to as Solid Models. ACP has the feature to map the ACP Composite Definitions onto external solid meshes.
In this section, the workflow of modeling mapped composite solid meshes is outlined. To a large extent the workflow is the same as that of a standard solid model, except there is one main difference: The solid mesh is imported via Mechanical Model and not generated in ACP (Pre) itself. See Solid Modeling.
An exemplary complete workflow contains these steps:
Pre-Processing: Define the Composite Definitions in ACP (Pre) as described in the Analysis of a Composite Solid Model section.
Mapping of the Composite Definitions: Import the external volume mesh and configure the Imported Solid Model object in ACP (Pre).
Analysis: Transfer the solid composite data to a downstream analysis (structural, modal, etc.).
Post-Processing: run the composite failure analysis for the composite structures in Mechanical.
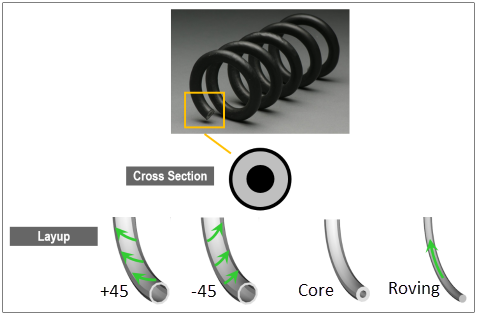
This example examines how a full cross-section composite spring can be modeled by mapping Composite Definitions from ACP (Pre) onto an existing mesh.
 You can download the Workbench archive for this example here:
Composite Spring
Project File
You can download the Workbench archive for this example here:
Composite Spring
Project File
Geometry and the Lay-Up
The geometry and the lay-up of the spring are shown in the figure below. The lay-up can be split into three sections. The four reinforcement plies at the outer surface consist of a woven fabric, and the total thickness of this section is 1 mm. The material orientation of the plies is alternating, +/- 45°. The next ply is a 2 mm thick isotropic core material. And a roving (carbon UD) fills the center section of the spring where the fibers are along the extrusion direction (helix) of the spring.