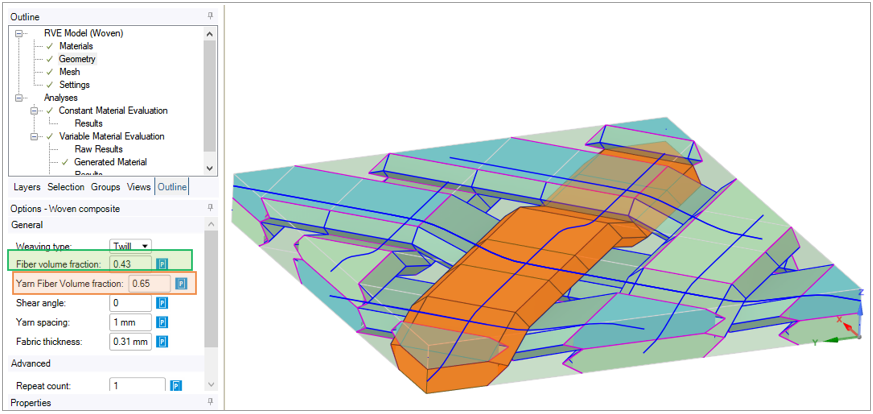
Woven composites consist of fiber material that has been woven together in two directions, surrounded by a matrix material. For the simulation, the fibers and the surrounding matrix material are grouped into a yarn material. The simulation is performed at the yarn level.
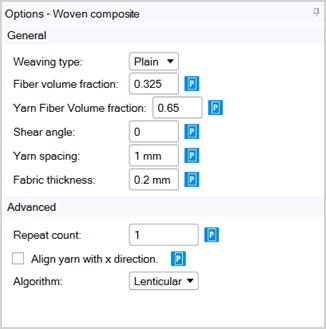
Weaving Type: The way in which the yarns are woven together.
Plain: Weft threads pass under one warp thread and then under one warp thread.
Twill: Weft threads pass over one or more warp threads and then under two or more warp threads.
Fiber Volume Fraction: The fraction of space within the RVE that the fiber material occupies.
Yarn Fiber Volume Fraction: The fraction of space within the yarn that the fiber material occupies.
Note: This should correspond to the fiber volume fraction of the constituent yarn material.
Shear Angle: The angle (in degrees) that the weave is sheared due to draping.
Yarn Spacing: The distance from one yarn to the next (from centers).
Fabric Thickness: The thickness of the woven fabric in the active unit system.
Repeat Count: The number of times that the unit cell is repeated in each coordinate direction.
Align Yarn With X Direction: When selected, weft threads are aligned with the global X-direction. Compare to Fabric Fiber Angle.
Algorithm: The algorithm to generate the RVE geometry. It influences both the cross-section of the yarn and the yarn path.
Choose the Simplified algorithm for the most robust and quick (but also least accurate) solution.
For high values of the fiber volume fraction, choose the Flattened Lenticular (high fiber volume fraction) algorithm.
Note: The relationship between the fiber volume fraction, the yarn volume fraction, and the fiber yarn volume fraction is as follows:
fiber volume fraction = yarn volume fraction * yarn fiber volume fraction.
Recommended Workflow for Woven Composites
This example is of a twill-woven RVE definition which provides further explanation on the concepts of fiber and yarn fiber volume fractions.
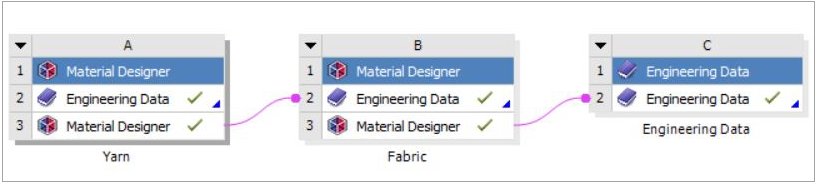 | |
| First Block | |
Contains the UD RVE to calculate the yarn's material properties that are later used in the woven composite RVE (fabric). |
 |
| Second Block | |
The woven composite RVE that uses the previously calculated yarn properties. |
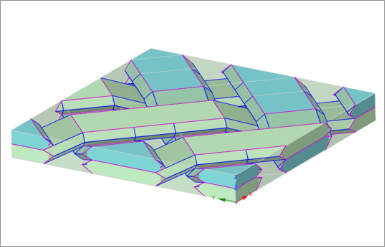 |
The yarn/UD properties are obtained from an upstream homogenization. Therefore, the yarn fiber volume fraction must match the UD RVE fiber volume fraction that is used in the previous Material Designer cell.
The total fiber volume fraction represents the actual total volume occupied by the fibers in the whole woven fabric, which contains yarns (made of fibers and resin) and the pure resin around the yarns that fill the remaining volume of the cuboid RVE. Note that only one yarn is highlighted in the following model and all the yarns are assigned the same yarn fiber volume fraction.