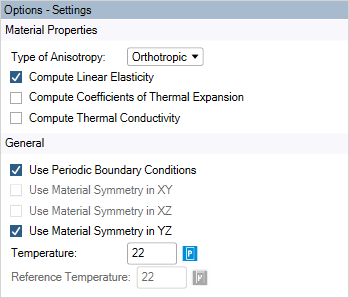
Use the Analysis Settings Dialog to configure the Homogenization Analysis. You can select which material properties will be computed as well as other options explained below.
Type of Anisotropy: The type of anisotropy of the homogenized material:
Orthotropic
Anisotropic
Compute Linear Elasticity: Compute the material constants for linear elasticity. For orthotropic materials, Material Designer computes engineering constants (Young’s moduli, shear moduli, Poisson’s ratios). For anisotropic materials, the stiffness matrix is computed.
Compute Coefficients of Thermal Expansion: Compute the orthotropic secant coefficients of thermal expansion (only available for orthotropic materials and if the linear elasticity is computed in addition).
Compute Thermal Conductivity: Compute the orthotropic thermal conductivity (only available for orthotropic materials).
Note: If possible, the density is computed in addition to the properties above. Similarly, if possible and if the thermal conductivity is computed, the specific heat is also computed.
Use Periodic Boundary Conditions: Apply periodic boundary conditions to the Finite Element Analysis.
Material Symmetry: Make use of symmetry to reduce the number of necessary load cases. (This option is not available for Analytical Homogenization.)
Temperature: Specify the environment temperature. This temperature is used to evaluate the material properties.
Reference Temperature: Specify the zero-thermal strain reference temperature. This is used for computing the coefficients of thermal expansion.
Note: If the Temperature and the Reference Temperature are equal, the Reference Temperature is slightly modified for the computation of the coefficients of thermal expansion.
For Analytical Homogenization, you can configure the following properties:
| CTE Homogenization Method: Choose the homogenization method that is used to compute the coefficients of thermal expansion. |
| Closure Approximation: Choose the type of closure approximation you want to use for the estimation of the fourth order orientation tensor in the orientations averaging. See also Computation of Material Properties. |